Description
Use the userScripts API to execute user scripts in the User Scripts context.
Permissions
userScriptsTo use the User Scripts API, chrome.userScripts, add the "userScripts" permission to your manifest.json and "host_permissions" for sites you want to run scripts on.
{ "name": "User script test extension", "manifest_version": 3, "minimum_chrome_version": "120", "permissions": [ "userScripts" ], "host_permissions": [ "*://example.com/*" ] } Availability
Concepts and usage
A user script is a snippet of code injected into a web page to modify its appearance or behavior. Unlike other extension features, such as Content Scripts and the chrome.scripting API, the User Scripts API lets you run arbitrary code. This API is required for extensions that run scripts provided by the user that cannot be shipped as part of your extension package.
Developer mode for extension users
As an extension developer, you already have Developer mode enabled in your installation of Chrome. For user script extensions, your users will also need to enable developer mode. Here are instructions that you can copy and paste into your own documentation.
- Go to the Extensions page by entering
chrome://extensionsin a new tab. (By designchrome://URLs are not linkable.) Enable Developer Mode by clicking the toggle switch next to Developer mode.
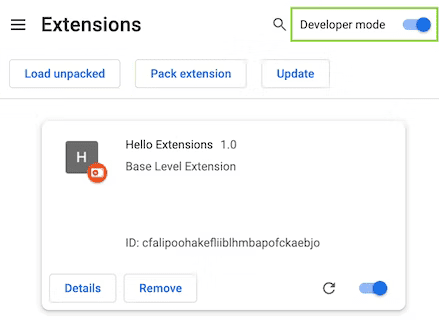
Extensions page (chrome://extensions)
You can determine if developer mode is enabled by checking whether chrome.userScripts throws an error. For example:
functionisUserScriptsAvailable(){try{// Property access which throws if developer mode is not enabled.chrome.userScripts;returntrue;}catch{// Not available.returnfalse;}}Work in isolated worlds
Both user and content scripts can run in an isolated world or in the main world. An isolated world is an execution environment that isn't accessible to a host page or other extensions. This lets a user script change its JavaScript environment without affecting the host page or other extensions' user and content scripts. Conversely, user scripts (and content scripts) are not visible to the host page or the user and content scripts of other extensions. Scripts running in the main world are accessible to host pages and other extensions and are visible to host pages and to other extensions. To select the world, pass "USER_SCRIPT" or "MAIN" when calling userScripts.register().
To configure a content security policy for the USER_SCRIPT world, call userScripts.configureWorld():
chrome.userScripts.configureWorld({csp:"script-src 'self'"});Messaging
Like content scripts and offscreen documents, user scripts communicate with other parts of an extension using messaging (meaning they can call runtime.sendMessage() and runtime.connect() as any other part of an extension would). However, they're received using dedicated event handlers (meaning, they don't use onMessage or onConnect). These handlers are called runtime.onUserScriptMessage and runtime.onUserScriptConnect. Dedicated handlers make it easier to identify messages from user scripts, which are a less-trusted context.
Before sending a message, you must call configureWorld() with the messaging argument set to true. Note that both the csp and messaging arguments can be passed at the same time.
chrome.userScripts.configureWorld({messaging:true});Extension updates
User scripts are cleared when an extension updates. You can add them back by running code in the runtime.onInstalled event handler in the extension service worker. Respond only to the "update" reason passed to the event callback.
Example
This example is from the userScript sample in our samples repository.
Register a script
The following example shows a basic call to register(). The first argument is an array of objects defining the scripts to be registered. There are more options than are shown here.
chrome.userScripts.register([{id:'test',matches:['*://*/*'],js:[{code:'alert("Hi!")'}]}]);Types
ExecutionWorld
The JavaScript world for a user script to execute within.
Enum
"MAIN" "USER_SCRIPT"
Specifies the execution environment of the DOM, which is the execution environment shared with the host page's JavaScript.
Specifies the execution environment that is specific to user scripts and is exempt from the page's CSP.
InjectionResult
Properties
- documentId
string
The document associated with the injection.
- error
string optional
The error, if any.
errorandresultare mutually exclusive. - frameId
number
The frame associated with the injection.
- result
any optional
The result of the script execution.
InjectionTarget
Properties
- allFrames
boolean optional
Whether the script should inject into all frames within the tab. Defaults to false. This must not be true if
frameIdsis specified. - documentIds
string[] optional
The IDs of specific documentIds to inject into. This must not be set if
frameIdsis set. - frameIds
number[] optional
The IDs of specific frames to inject into.
- tabId
number
The ID of the tab into which to inject.
RegisteredUserScript
Properties
- allFrames
boolean optional
If true, it will inject into all frames, even if the frame is not the top-most frame in the tab. Each frame is checked independently for URL requirements; it will not inject into child frames if the URL requirements are not met. Defaults to false, meaning that only the top frame is matched.
- excludeGlobs
string[] optional
Specifies wildcard patterns for pages this user script will NOT be injected into.
- excludeMatches
string[] optional
Excludes pages that this user script would otherwise be injected into. See Match Patterns for more details on the syntax of these strings.
- id
string
The ID of the user script specified in the API call. This property must not start with a '_' as it's reserved as a prefix for generated script IDs.
- includeGlobs
string[] optional
Specifies wildcard patterns for pages this user script will be injected into.
- js
ScriptSource[] optional
The list of ScriptSource objects defining sources of scripts to be injected into matching pages. This property must be specified for ${ref:register}, and when specified it must be a non-empty array.
- matches
string[] optional
Specifies which pages this user script will be injected into. See Match Patterns for more details on the syntax of these strings. This property must be specified for ${ref:register}.
- runAt
RunAt optional
Specifies when JavaScript files are injected into the web page. The preferred and default value is
document_idle. - world
ExecutionWorld optional
The JavaScript execution environment to run the script in. The default is
`USER_SCRIPT`. - worldId
string optional
Chrome 133+Specifies the user script world ID to execute in. If omitted, the script will execute in the default user script world. Only valid if
worldis omitted or isUSER_SCRIPT. Values with leading underscores (_) are reserved.
ScriptSource
Properties
- code
string optional
A string containing the JavaScript code to inject. Exactly one of
fileorcodemust be specified. - file
string optional
The path of the JavaScript file to inject relative to the extension's root directory. Exactly one of
fileorcodemust be specified.
UserScriptFilter
Properties
- ids
string[] optional
getScriptsonly returns scripts with the IDs specified in this list.
UserScriptInjection
Properties
- injectImmediately
boolean optional
Whether the injection should be triggered in the target as soon as possible. Note that this is not a guarantee that injection will occur prior to page load, as the page may have already loaded by the time the script reaches the target.
- js
The list of ScriptSource objects defining sources of scripts to be injected into the target.
- target
Details specifying the target into which to inject the script.
- world
ExecutionWorld optional
The JavaScript "world" to run the script in. The default is
USER_SCRIPT. - worldId
string optional
Specifies the user script world ID to execute in. If omitted, the script will execute in the default user script world. Only valid if
worldis omitted or isUSER_SCRIPT. Values with leading underscores (_) are reserved.
WorldProperties
Properties
- csp
string optional
Specifies the world csp. The default is the
`ISOLATED`world csp. - messaging
boolean optional
Specifies whether messaging APIs are exposed. The default is
false. - worldId
string optional
Chrome 133+Specifies the ID of the specific user script world to update. If not provided, updates the properties of the default user script world. Values with leading underscores (
_) are reserved.
Methods
configureWorld()
chrome.userScripts.configureWorld(
properties: WorldProperties,
callback?: function,
)
Configures the `USER_SCRIPT` execution environment.
Parameters
- properties
Contains the user script world configuration.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:() => void
Returns
Promise<void>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
execute()
chrome.userScripts.execute(
injection: UserScriptInjection,
callback?: function,
)
Injects a script into a target context. By default, the script will be run at document_idle, or immediately if the page has already loaded. If the injectImmediately property is set, the script will inject without waiting, even if the page has not finished loading. If the script evaluates to a promise, the browser will wait for the promise to settle and return the resulting value.
Parameters
- injection
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:(result: InjectionResult[]) => void
- result
Returns
Promise<InjectionResult[]>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
getScripts()
chrome.userScripts.getScripts(
filter?: UserScriptFilter,
callback?: function,
)
Returns all dynamically-registered user scripts for this extension.
Parameters
- filter
UserScriptFilter optional
If specified, this method returns only the user scripts that match it.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:(scripts: RegisteredUserScript[]) => void
- scripts
Returns
Promise<RegisteredUserScript[]>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
getWorldConfigurations()
chrome.userScripts.getWorldConfigurations(
callback?: function,
)
Retrieves all registered world configurations.
Parameters
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:(worlds: WorldProperties[]) => void
- worlds
Returns
Promise<WorldProperties[]>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
register()
chrome.userScripts.register(
scripts: RegisteredUserScript[],
callback?: function,
)
Registers one or more user scripts for this extension.
Parameters
- scripts
Contains a list of user scripts to be registered.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:() => void
Returns
Promise<void>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
resetWorldConfiguration()
chrome.userScripts.resetWorldConfiguration(
worldId?: string,
callback?: function,
)
Resets the configuration for a user script world. Any scripts that inject into the world with the specified ID will use the default world configuration.
Parameters
- worldId
string optional
The ID of the user script world to reset. If omitted, resets the default world's configuration.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:() => void
Returns
Promise<void>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
unregister()
chrome.userScripts.unregister(
filter?: UserScriptFilter,
callback?: function,
)
Unregisters all dynamically-registered user scripts for this extension.
Parameters
- filter
UserScriptFilter optional
If specified, this method unregisters only the user scripts that match it.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:() => void
Returns
Promise<void>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
update()
chrome.userScripts.update(
scripts: RegisteredUserScript[],
callback?: function,
)
Updates one or more user scripts for this extension.
Parameters
- scripts
Contains a list of user scripts to be updated. A property is only updated for the existing script if it is specified in this object. If there are errors during script parsing/file validation, or if the IDs specified do not correspond to a fully registered script, then no scripts are updated.
- callback
function optional
The
callbackparameter looks like:() => void
Returns
Promise<void>
Promises are supported in Manifest V3 and later, but callbacks are provided for backward compatibility. You cannot use both on the same function call. The promise resolves with the same type that is passed to the callback.
