Software Project Management (SPM) – Software Engineering
Last Updated : 17 Nov, 2024
Software Project Management (SPM) is a proper way of planning and leading software projects. It is a part of project management in which software projects are planned, implemented, monitored, and controlled. This article focuses on discussing Software Project Management (SPM).
Need for Software Project Management
Software is a non-physical product. Software development is a new stream in business and there is very little experience in building software products. Most of the software products are made to fit clients’ requirements. The most important is that basic technology changes and advances so frequently and rapidly that the experience of one product may not be applied to the other one.
Such types of business and environmental constraints increase risk in software development hence it is essential to manage software projects efficiently. It is necessary for an organization to deliver quality products, keep the cost within the client’s budget constraint, and deliver the project as per schedule. Hence, in order, software project management is necessary to incorporate user requirements along with budget and time constraints.
Types of Management in SPM
1. Conflict Management
Conflict management is the process to restrict the negative features of conflict while increasing the positive features of conflict. The goal of conflict management is to improve learning and group results including efficacy or performance in an organizational setting. Properly managed conflict can enhance group results.
2. Risk Management
Risk management is the analysis and identification of risks that is followed by synchronized and economical implementation of resources to minimize, operate and control the possibility or effect of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities.
3. Requirement Management
It is the process of analyzing, prioritizing, tracking, and documenting requirements and then supervising change and communicating to pertinent stakeholders. It is a continuous process during a project.
4. Change Management
Change management is a systematic approach to dealing with the transition or transformation of an organization’s goals, processes, or technologies. The purpose of change management is to execute strategies for effecting change, controlling change, and helping people to adapt to change.
5. Software Configuration Management
Software configuration management is the process of controlling and tracking changes in the software, part of the larger cross-disciplinary field of configuration management. Software configuration management includes revision control and the inauguration of baselines.
6. Release Management
Release Management is the task of planning, controlling, and scheduling the built-in deploying releases. Release management ensures that the organization delivers new and enhanced services required by the customer while protecting the integrity of existing services.
Aspects of Software Project Management
The list of focus areas it can tackle and the broad upsides of Software Project Management is:
1. Planning
The software project manager lays out the complete project’s blueprint. The project plan will outline the scope, resources, timelines, techniques, strategy, communication, testing, and maintenance steps. SPM can aid greatly here.
2. Leading
A software project manager brings together and leads a team of engineers, strategists, programmers, designers, and data scientists. Leading a team necessitates exceptional communication, interpersonal, and leadership abilities. One can only hope to do this effectively if one sticks with the core SPM principles.
3. Execution
SPM comes to the rescue here also as the person in charge of software projects (if well versed with SPM/Agile methodologies) will ensure that each stage of the project is completed successfully. measuring progress, monitoring to check how teams function, and generating status reports are all part of this process.
4. Time Management
Abiding by a timeline is crucial to completing deliverables successfully. This is especially difficult when managing software projects because changes to the original project charter are unavoidable over time. To assure progress in the face of blockages or changes, software project managers ought to be specialists in managing risk and emergency preparedness. This Risk Mitigation and
management is one of the core tenets of the philosophy of SPM.
5. Budget
Software project managers, like conventional project managers, are responsible for generating a project budget and adhering to it as closely as feasible, regulating spending, and reassigning funds as needed. SPM teaches us how to effectively manage the monetary aspect of projects to avoid running into a financial crunch later on in the project.
6. Maintenance
Software project management emphasizes continuous product testing to find and repair defects early, tailor the end product to the needs of the client, and keep the project on track. The software project manager makes ensuring that the product is thoroughly tested, analyzed, and adjusted as needed. Another point in favor of SPM.
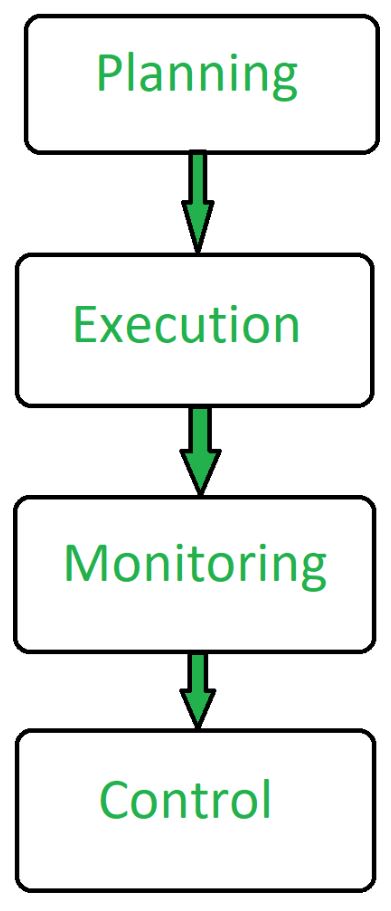
Aspects of Project Management
Downsides of Software Project Management
Numerous issues can develop if a Software project manager lacks the necessary expertise or knowledge. Software Project management has several drawbacks, including resource loss, scheduling difficulty, data protection concerns, and interpersonal conflicts between Developers/Engineers/Stakeholders. Furthermore, outsourcing work or recruiting additional personnel to complete the project may result in hefty costs for one’s company.
1. Costs are High
Consider spending money on various kinds of project management tools, software, & services if ones engage in Software Project Management strategies. These initiatives can be expensive and time-consuming to put in place. Because your team will be using them as well, they may require training. One may need to recruit subject-matter experts or specialists to assist with a project, depending on the circumstances. Stakeholders will frequently press for the inclusion of features that were not originally envisioned. All of these factors can quickly drive up a project’s cost.
2. Complexity will be increased
Software Project management is a multi-stage, complex process. Unfortunately, some specialists might have a propensity to overcomplicate everything, which can lead to confusion among teams and lead to delays in project completion. Their expressions are very strong and specific in their ideas, resulting in a difficult work atmosphere. Projects having a larger scope are typically more arduous to complete, especially if there isn’t a dedicated team committed completely to the project. Members of cross-functional teams may lag far behind their daily tasks, adding to the overall complexity of the project being worked on.
3. Overhead in Communication
Recruits enter your organization when we hire software project management personnel. This provides a steady flow of communication that may or may not match a company’s culture. As a result, it is advised that you maintain your crew as
small as feasible. The communication overhead tends to skyrocket when a team becomes large enough. When a large team is needed for a project, it’s critical to identify software project managers who can conduct effective communication with a variety of people.
4. Lack of Originality
Software Project managers can sometimes provide little or no space for creativity. Team leaders either place an excessive amount of emphasis on management processes or impose hard deadlines on their employees, requiring them to develop and operate code within stringent guidelines. This can stifle innovative thought and innovation that could be beneficial to the project. When it comes to Software project management, knowing when to encourage creativity and when to stick to the project plan is crucial. Without Software project management personnel, an organization can perhaps build and ship code more quickly. However, employing a trained specialist to handle these areas, on the other hand, can open up new doors and help the organization achieve its objectives more
quickly and more thoroughly.
Question For Practice
(A) 110.54
(B) 408.74
(C) 304.78
(D) 220.14
Solution: Correct Answer is (B).
Similar Reads
Software Engineering Tutorial
Software Engineering is a subdomain of Engineering in which you learn to develop, design, test, and maintain software using a systematic and structured approach. Software is a collection of programs. And that programs are developed by software engineers. The code of a program is written in any of va
7 min read
Introduction
Introduction to Software Engineering
Software is a program or set of programs containing instructions that provide the desired functionality. Engineering is the process of designing and building something that serves a particular purpose and finds a cost-effective solution to problems. Table of Content What is Software Engineering?Key
11 min read
What is the Need of Software Engineering?
Pre-requisites: Software Engineering | Introduction to Software Engineering Software engineering is a technique through which we can develop or create software for computer systems or any other electronic devices. It is a systematic, scientific and disciplined approach to the development, functionin
4 min read
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Software development life cycle (SDLC) is a structured process that is used to design, develop, and test good-quality software. SDLC, or software development life cycle, is a methodology that defines the entire procedure of software development step-by-step. The goal of the SDLC life cycle model is
11 min read
Classification of Software - Software Engineering
Software Engineering is the process of developing a software product in a well-defined systematic approach software engineering is the process of analyzing user needs and then designing, constructing, and testing end-user applications that will satisfy these needs through the use of software program
8 min read
Software Characteristics - Software Engineering
Software is defined as a collection of computer programs, procedures, rules, and data. Software Characteristics are classified into six major components. Software engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software. In this article, we will look into the characteri
6 min read
Software Quality - Software Engineering
Traditionally, a high-quality product is outlined in terms of its fitness of purpose. That is, a high-quality product will specifically be what the users need to try. For code products, the fitness of purpose is typically taken in terms of satisfaction of the wants arranged down within the SRS docum
5 min read
ISO/IEC 9126 in Software Engineering
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established a series of ISO and ISO/IEC standards for software quality. Starting with the ISO 9000-3 instructions for implementing the ISO 9001 standard, which is concerned with quality assurance processes, to the creation, supply, install
4 min read
Boehm's Software Quality Model
In 1978, B.W. Boehm introduced his software quality model, which defines software quality through a hierarchical structure of attributes and metrics. This model is similar to the McCall Quality Model but encompasses a wider range of characteristics, including hardware performance-related ones. Boehm
4 min read
McCall's Quality Model
McCall's Quality Model is one of the software quality models. McCall's Quality Model aims to cover the gap between users and developers by highlighting several kinds of software quality factors that reflect both the views of users and developers' interests. Table of Content What is McCall's Software
4 min read
Software Crisis - Software Engineering
The term "software crisis" refers to the numerous challenges and difficulties faced by the software industry during the 1960s and 1970s. It became clear that old methods of developing software couldn't keep up with the growing complexity and demands of new projects. This led to high costs, delays, a
3 min read
Difference between Software Engineering process and Conventional Engineering Process
Software Engineering Process and Conventional Engineering Process, both are processes related to computers and development. In this article, we will see the similarities as well as differences between both, that is Software Engineering Process and the Conventional Engineering Process. Table of Conte
4 min read
Software Measurement and Metrics
Software Measurement and Metrics
Software Measurement: A measurement is a manifestation of the size, quantity, amount, or dimension of a particular attribute of a product or process. Software measurement is a titrate impute of a characteristic of a software product or the software process. Table of Content Software Measurement Prin
4 min read
People Metrics and Process Metrics in Software Engineering
People Metrics and Process Metrics, both play important roles in software development. People Metrics helps in quantifying the useful attributes whereas Process Metrics creates the body of the software. People metrics focus on how well team members work together and their overall satisfaction, while
8 min read
Halstead’s Software Metrics - Software Engineering
Halstead's Software metrics are a set of measures proposed by Maurice Halstead to evaluate the complexity of a software program. These metrics are based on the number of distinct operators and operands in the program and are used to estimate the effort required to develop and maintain the program. T
11 min read
Cyclomatic Complexity
Cyclomatic complexity, developed by Thomas McCabe, is a metric that measures the complexity of a program by counting its decision points. It measures the number of unique paths through the code, indicating how complex the logic is. Lower complexity suggests simpler, more manageable code, reducing th
6 min read
Functional Point (FP) Analysis - Software Engineering
Functional Point Analysis (FPA) is a software measurement technique used to assess the size and complexity of a software system based on its functionality. It involves categorizing the functions of the software, such as input screens, output reports, inquiries, files, and interfaces, and assigning w
9 min read
Lines of Code (LOC) in Software Engineering
A line of code (LOC) is any line of text in a code that is not a comment or blank line, and also header lines, in any case of the number of statements or fragments of statements on the line. LOC consists of all lines containing the declaration of any variable, and executable and non-executable state
4 min read
Software Development Models
Agile Software Development
Agile Software Development - Software Engineering
Agile Software Development is a software development methodology that values flexibility, collaboration, and customer satisfaction. It is based on the Agile Manifesto, a set of principles for software development that prioritize individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration,
13 min read
Agile Development Models - Software Engineering
In earlier days, the Iterative Waterfall Model was very popular for completing a project. But nowadays, developers face various problems while using it to develop software. The main difficulties included handling customer change requests during project development and the high cost and time required
11 min read
Agile Methodology Advantages and Disadvantages
Agile Software Development Methodology is a process of software development similar to other software development methodologies like waterfall models, V-models, iterative models, etc. Agile methodology follows the iterative as well as incremental approach that emphasizes the importance of delivering
4 min read
Agile SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle)
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process of maintaining or building software applications/services/systems. Generally, it includes various levels, from initial development plan and analysis to post-development software testing and evaluation. It also consists of the models and methodologi
8 min read
Difference between Traditional and Agile Software Development
Traditional Software Development and Agile Software Development are the ways of the designing and developing system software. Both are important types of the software designing. Traditional Software DevelopmentTraditional Software Development is the software development process used to design and de
5 min read
Comparison between Agile model and other models in Software Engineering
Software development models are various processes or methods that are chosen for project development depending on the objectives and goals of the project. Agile is a popular model among these development models because it is flexible and adapts quickly to changes. It focuses on delivering small, usa
8 min read
Software Requirements Specification
Software Requirement Specification (SRS) Format
In order to form a good SRS, here you will see some points that can be used and should be considered to form a structure of good Software Requirements Specification (SRS). These are below mentioned in the table of contents and are well explained below. Table of ContentIntroductionGeneral description
5 min read
Parts of a SRS document - Software Engineering
The important parts of the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document are: Functional requirements of the systemNon-functional requirements of the system, andGoals of implementationThese are explained as follows. Functional RequirementsThe purposeful requirements part discusses the functiona
2 min read
Classification of Software Requirements - Software Engineering
Classification of Software Requirements is important in the software development process. It organizes our requirements into different categories that make them easier to manage, prioritize, and track. The main types of Software Requirements are functional, non-functional, and domain requirements. T
8 min read
How to write a good SRS for your Project
What is SRS? A software requirements specification (SRS) is a description of a software system to be developed. It lays out functional and non-functional requirements and may include a set of use cases that describe user interactions that the software must provide. The output of requirement engineer
8 min read
Software Engineering | Quality Characteristics of a good SRS
Related Article: Writing a good SRS for your project Quality characteristics of a good Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document include:Complete: The SRS should include all the requirements for the software system, including both functional and non-functional requirements.Consistent: The S
7 min read
Difference between SRS and FRS
The role of formulating a document is to understand requirements that will be compelled to develop a robust software. Type of document required depends upon business type, their criteria, how company processes, and what class of software is to be developed. Let us understand common documents which a
3 min read
Software Project Management(SPM)
Software Project Management (SPM) - Software Engineering
Software Project Management (SPM) is a proper way of planning and leading software projects. It is a part of project management in which software projects are planned, implemented, monitored, and controlled. This article focuses on discussing Software Project Management (SPM). Table of Content Types
7 min read
Project Size Estimation Techniques - Software Engineering
In the fast-paced world of Software Engineering, accurately estimating the size of a project is key to its success. Understanding how big a project will be helps predict the resources, time, and cost needed, ensuring the project starts off on the right foot. Project Size Estimation Techniques are vi
12 min read
System configuration management - Software Engineering
Whenever software is built, there is always scope for improvement and those improvements bring picture changes. Changes may be required to modify or update any existing solution or to create a new solution for a problem. Requirements keep on changing daily so we need to keep on upgrading our systems
7 min read
COCOMO Model - Software Engineering
The Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) It was proposed by Barry Boehm in 1981 and is based on the study of 63 projects, which makes it one of the best-documented models. It is a Software Cost Estimation Model that helps predict the effort, cost, and schedule required for a software development project
15+ min read
Capability Maturity Model (CMM) - Software Engineering
The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a tool used to improve and refine software development processes. It provides a structured way for organizations to assess their current practices and identify areas for improvement. CMM consists of five maturity levels: initial, repeatable, defined, managed, a
11 min read
Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 1
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a conceptual model for defining the tasks performed at each step of the software development process. This model gives you a brief about the life cycle of Software in the development phase. In this particular article, we are going to discuss risk managem
8 min read
Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 2
Prerequisite: Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 1 We have seen the Risk Management Techniques in SDLC which we have discussed Preliminary Analysis, System Analysis, and Requirement Definition part. In this article, we will be discussing the System Design and Development phase of the Software
9 min read
Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 3
Prerequisite - Integrating Risk Management in SDLC | Set 1, and Set 2. We have already discussed the first four steps of the Software Development Life Cycle. In this article, we will be discussing the remaining four steps: Integration and System Testing, Installation, Operation and Acceptance Testin
9 min read
Software Project Management Complexities | Software Engineering
Software project management complexities refer to the various challenges and difficulties involved in managing software development projects. The primary goal of software project management is to guide a team of developers to complete a project successfully within a given timeframe. However, this ta
12 min read
Quasi renewal processes - Software Engineering
Let {N(t), t > 0} be a counting process and let [Tex]$X_n$ [/Tex]be the time between the [Tex]$(n-1)_{th}$ [/Tex]and the [Tex]$n_{th}$ [/Tex]event of this process, [Tex]n\geq 1 [/Tex] Definition: If the sequence of non-negative random variables {X1, X2, ....} is independent and [Tex]$$X_i=aX_{i-1
7 min read
Reliability Growth Models - Software Engineering
The reliability growth group of models measures and predicts the improvement of reliability programs through the testing process. The growth model represents the reliability or failure rate of a system as a function of time or the number of test cases. Models included in this group are as follows. C
5 min read
Jelinski Moranda software reliability model - Software Engineering
The Jelinski-Moranda (JM) Software Reliability Model is a mathematical model developed in 1972 by M.A. Jelinski and P.A. Moranda. It is used to predict the reliability of software systems, particularly during the testing and debugging phases. This model assumes that software failures occur randomly
10 min read
Software Engineering | Schick-Wolverton software reliability model
Prerequisite - Jelinski Moranda software reliability model The Schick-Wolverton (S-W) model is a modification to the J-M model. It is similar to the J-M model except that it further assumes that the failure rate at the ith time interval increases with time ti since the last debugging. In the model,
4 min read
Goel-Okumoto Model - Software Engineering
The Goel-Okumoto Model is a reliable software prediction tool based on simple principles: bugs are independent, bug detection is related to existing bugs, and bugs are fixed promptly. Through mathematical estimation, it helps predict bug counts and manage software development effectively, offering e
7 min read
Mills' Error Seeding Model - Software Engineering
Mills'error seeding model proposed an error seeding method to estimate the number of errors in a program by introducing seeded errors into the program. From the debugging data, which consists of inherent errors and induced errors, the unknown number of inherent errors could be estimated. If both inh
7 min read
Basic Fault Tolerant Software Techniques
Fault tolerance is a critical property of software systems, ensuring they can continue operating even when faced with failures or errors. This resilience is achieved through various techniques to prevent disruptions and maintain high availability, particularly for mission-critical applications. Basi
11 min read
Software Maintenance - Software Engineering
Software Maintenance refers to the process of modifying and updating a software system after it has been delivered to the customer. This involves fixing bugs, adding new features, and adapting to new hardware or software environments. Effective maintenance is crucial for extending the software's lif
14 min read
Software Testing and Debugging
What is Software Testing?
Software testing is an important process in the Software Development Lifecycle(SDLC). It involves verifying and validating that a Software Application is free of bugs, meets the technical requirements set by its Design and Development, and satisfies user requirements efficiently and effectively. Her
11 min read
Types of Software Testing
Software Testing is an important part of the Software Development Lifecycle, which includes many more Types of Software Testing that we are discussing here in detail. Read More: Software Development Life Cycle. Table of Content Different Types of Software Testing1. Manual Testing 2. Automation Testi
15+ min read
Principles of Software testing - Software Testing
Software testing is an important aspect of software development, ensuring that applications function correctly and meet user expectations. In this article, we will go into the principles of software testing, exploring key concepts and methodologies to enhance product quality. From test planning to e
10 min read
Testing Guidelines - Software Engineering
Software testing is an essential component of software development, ensuring that applications function correctly, meet user expectations, and are ready for deployment. Effective software testing involves a structured approach guided by well-defined principles and best practices. This article explor
3 min read
Black Box Testing - Software Engineering
Black Box Testing is a Software testing method in which the internal working of the application is not known to the tester. The Black Box Testing mainly focuses on testing the functionality of software without any knowledge of the internal logic of an application. Here we are learning the topics rel
12 min read
White box Testing - Software Engineering
White box testing techniques analyze the internal structures the used data structures, internal design, code structure, and the working of the software rather than just the functionality as in black box testing. It is also called glass box testing clear box testing or structural testing. White Box T
15 min read
Unit Testing - Software Testing
Unit Testing is a software testing technique in which individual units or components of a software application are tested in isolation. These units are the smallest pieces of code, typically functions or methods, ensuring they perform as expected. Unit testing helps identify bugs early in the develo
12 min read
Acceptance Testing - Software Testing
Acceptance Testing is an important aspect of Software Testing, which guarantees that software aligns with user needs and business requirements. The major aim of this test is to evaluate the compliance of the system with the business requirements and assess whether it is acceptable for delivery or no
5 min read
Alpha Testing - Software Testing
Alpha Testing is an essential phase in software testing conducted by the development or QA team before beta testing . It aims to identify and fix bugs in a controlled environment that simulates real-world conditions. This helps ensure the software's functionality , reliability , and stability . Alph
8 min read
Beta Testing - Software Testing
Prerequisites: Software Testing Basics, Types of Software Testing Table of Content IntroductionWhy require Beta Testing?Characteristics of Beta TestingTypes of Beta TestingCriteria for Beta TestingTools used for Beta TestingUses of Beta TestingAdvantages of Beta TestingDisadvantages of Beta TestingI
6 min read
Regression Testing - Software Engineering
Regression testing is a crucial aspect of software engineering that ensures the stability and reliability of a software product. It involves retesting the previously tested functionalities to verify that recent code changes haven't adversely affected the existing features. By identifying and fixing
7 min read
Integration Testing - Software Engineering
Integration testing is the process of testing the interface between two software units or modules. It focuses on determining the correctness of the interface. The purpose of integration testing is to expose faults in the interaction between integrated units. Once all the modules have been unit-teste
11 min read
What is Debugging in Software Engineering?
Debugging in Software Engineering is the process of identifying and resolving errors or bugs in a software system. It's a critical aspect of software development, ensuring quality, performance, and user satisfaction. Despite being time-consuming, effective debugging is essential for reliable and com
11 min read
Software Verification and Validation
Software Engineering Interview Questions