What is the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on global carbon emissions?
- PMID: 34752864
- PMCID: PMC8572037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151503
What is the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on global carbon emissions?
Abstract
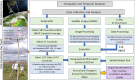
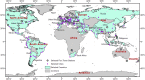
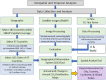
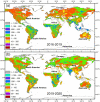
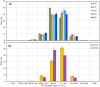
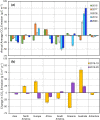
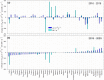
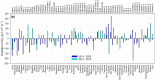
The coronavirus 2019 (COVID 19, or SARS-CoV-2) pandemic that started in December 2019 has caused an unprecedented impact in most countries globally and continues to threaten human lives worldwide. The COVID-19 and strict lockdown measures have had adverse effects on human health and national economies. These lockdown measures have played a critical role in improving air quality, water quality, and the ozone layer and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Using Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) Level 4 carbon (SMAP LC4) satellite products, this study investigated the impacts of COVID-19 lockdown measures on annual carbon emissions globally, focusing on 47 greatly affected countries and their 105 cities by December 2020. It is shown that while the lockdown measures significantly reduced carbon emissions globally, several countries and cities observed this reduction as temporary because strict lockdown measures were not imposed for extended periods in 2020. Overall, the total carbon emissions of select 184 countries reduced by 438 Mt in 2020 than in 2019. Since the global economic activities are slowly expected to return to the non-COVID-19 state, the reduction in carbon emissions during the pandemic will not be sustainable in the long run. For sustainability, concerned authorities have to put significant efforts to change transportation, climate, and environmental policies globally that fuel carbon emissions. Overall, the presented results provide directions to the stakeholders and policymakers to develop and implement measures to control carbon emissions for a sustainable environment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Carbon emission; Greenhouse gas; Lockdown; Pandemic; SMAP.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
- Implications of COVID-19 on global environmental pollution and carbon emissions with strategies for sustainability in the COVID-19 era.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Feb 25;809:151657. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151657. Epub 2021 Nov 16.Sci Total Environ. 2022.PMID: 34793787Free PMC article.Review.
- A global observational analysis to understand changes in air quality during exceptionally low anthropogenic emission conditions.Environ Int. 2021 Dec;157:106818. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106818. Epub 2021 Aug 20.Environ Int. 2021.PMID: 34425482
- Geospatial analysis of COVID-19 lockdown effects on air quality in the South and Southeast Asian region.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Feb 20;756:144009. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144009. Epub 2020 Nov 21.Sci Total Environ. 2021.PMID: 33250248Free PMC article.
- A mini-review: positive impact of COVID-19 on Arial health and ecology.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jun;29(27):40520-40530. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19961-x. Epub 2022 Mar 29.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022.PMID: 35349061Free PMC article.Review.
- The impact of COVID 19 on air pollution levels and other environmental indicators - A case study of Egypt.J Environ Manage. 2021 Jan 1;277:111496. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111496. Epub 2020 Oct 10.J Environ Manage. 2021.PMID: 33069147Free PMC article.
Cited by
- COP26: Progress, Challenges, and Outlook.Adv Atmos Sci. 2022;39(8):1209-1216. doi: 10.1007/s00376-022-2097-z. Epub 2022 Jun 27.Adv Atmos Sci. 2022.PMID: 35789623Free PMC article.
- The impact of financial tools in environmental degradation management: the relationship between Co2 emission and ESG funds.Environ Dev Sustain. 2023 Apr 12:1-16. doi: 10.1007/s10668-023-03229-6. Online ahead of print.Environ Dev Sustain. 2023.PMID: 37363026Free PMC article.
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on global trade-embodied carbon emissions.J Clean Prod. 2023 Jul 1;408:137042. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137042. Epub 2023 Apr 5.J Clean Prod. 2023.PMID: 37077939Free PMC article.
- Rural Farmers' Cognition and Climate Change Adaptation Impact on Cash Crop Productivity: Evidence from a Recent Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 1;19(19):12556. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912556.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022.PMID: 36231854Free PMC article.
- Climate change and COVID-19: Interdisciplinary perspectives from two global crises.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Oct 20;844:157142. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157142. Epub 2022 Jul 5.Sci Total Environ. 2022.PMID: 35798107Free PMC article.Review.
References
- Anderson T.R., Hawkins E., Jones P.D. CO2, the greenhouse effect and global warming: from the pioneering work of Arrhenius and Callendar to today's earth system models. Endeavour. 2016;40:178–187. - PubMed
- Balasubramaniam D., Kanmanipappa C., Shankarlal B., Saravanan M. Assessing the impact of lockdown in US, Italy and France– what are the changes in air quality? Energy Sources Part A. 2020:1–11.
- Baldasano J.M. COVID-19 lockdown effects on air quality by NO2 in the cities of Barcelona and Madrid (Spain) Sci. Total Environ. 2020;741 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

