Sentimental Analysis of COVID-19 Tweets Using Deep Learning Models
- PMID: 33916139
- PMCID: PMC8167749
- DOI: 10.3390/idr13020032
Sentimental Analysis of COVID-19 Tweets Using Deep Learning Models
Abstract
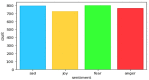
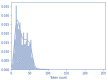
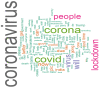
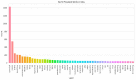
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an ongoing pandemic with large global attention. However, spreading false news on social media sites like Twitter is creating unnecessary anxiety towards this disease. The motto behind this study is to analyses tweets by Indian netizens during the COVID-19 lockdown. The data included tweets collected on the dates between 23 March 2020 and 15 July 2020 and the text has been labelled as fear, sad, anger, and joy. Data analysis was conducted by Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model, which is a new deep-learning model for text analysis and performance and was compared with three other models such as logistic regression (LR), support vector machines (SVM), and long-short term memory (LSTM). Accuracy for every sentiment was separately calculated. The BERT model produced 89% accuracy and the other three models produced 75%, 74.75%, and 65%, respectively. Each sentiment classification has accuracy ranging from 75.88-87.33% with a median accuracy of 79.34%, which is a relatively considerable value in text mining algorithms. Our findings present the high prevalence of keywords and associated terms among Indian tweets during COVID-19. Further, this work clarifies public opinion on pandemics and lead public health authorities for a better society.
Keywords: BERT; COVID-19; lockdown; sentimental analysis; word cloud.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
- Vaccine sentiment analysis using BERT + NBSVM and geo-spatial approaches.J Supercomput. 2023 May 7:1-31. doi: 10.1007/s11227-023-05319-8. Online ahead of print.J Supercomput. 2023.PMID: 37359330Free PMC article.
- Identifying Potential Lyme Disease Cases Using Self-Reported Worldwide Tweets: Deep Learning Modeling Approach Enhanced With Sentimental Words Through Emojis.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Oct 16;25:e47014. doi: 10.2196/47014.J Med Internet Res. 2023.PMID: 37843893Free PMC article.
- Opinion analysis and aspect understanding during covid-19 pandemic using BERT-Bi-LSTM ensemble method.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 12;12(1):17095. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21604-7.Sci Rep. 2022.PMID: 36224328Free PMC article.
- COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy: A Global Public Health and Risk Modelling Framework Using an Environmental Deep Neural Network, Sentiment Classification with Text Mining and Emotional Reactions from COVID-19 Vaccination Tweets.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 May 12;20(10):5803. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20105803.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023.PMID: 37239532Free PMC article.
- Applying Machine Learning to Identify Anti-Vaccination Tweets during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 12;18(8):4069. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084069.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021.PMID: 33921539Free PMC article.
Cited by
- A hybrid transformer and attention based recurrent neural network for robust and interpretable sentiment analysis of tweets.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):24882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76079-5.Sci Rep. 2024.PMID: 39438715Free PMC article.
- Sentiment Analysis of Social Media Data on Ebola Outbreak Using Deep Learning Classifiers.Life (Basel). 2024 May 30;14(6):708. doi: 10.3390/life14060708.Life (Basel). 2024.PMID: 38929691Free PMC article.
- How the COVID-19 pandemic signaled the demise of Antarctic exceptionalism.Sci Adv. 2024 Mar;10(9):eadk4424. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk4424. Epub 2024 Mar 1.Sci Adv. 2024.PMID: 38427734Free PMC article.
- Leveraging Tweets for Artificial Intelligence Driven Sentiment Analysis on the COVID-19 Pandemic.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 May 13;10(5):910. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10050910.Healthcare (Basel). 2022.PMID: 35628045Free PMC article.
- Deep Learning-Based Mental Health Model on Primary and Secondary School Students' Quality Cultivation.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 6;2022:7842304. doi: 10.1155/2022/7842304. eCollection 2022.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022.PMID: 35845877Free PMC article.
References
- Chawla S., Mittal M., Chawla M., Goyal L. Corona Virus-SARS-CoV-2: An Insight to Another way of Natural Disaster. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 2020;6 doi: 10.4108/eai.28-5-2020.164823. - DOI
- Socio-Economic Impact of COVID-19|UNDP. [(accessed on 15 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/coronavirus/socio-economic-imp....
- Staszkiewicz P., Chomiak-Orsa I. Dynamics of the COVID-19 Contagion and Mortality: Country Factors, Social Media, and Market Response Evidence from a Global Panel Analysis. IEEE Access. 2020;8:106009–106022. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2999614. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources