The socioeconomic and environmental drivers of the COVID-19 pandemic: A review
- PMID: 33507498
- PMCID: PMC7841383
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-020-01497-4
The socioeconomic and environmental drivers of the COVID-19 pandemic: A review
Abstract
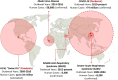
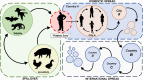
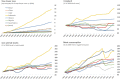
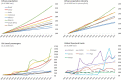
In recent decades, there has been an intensification of the socioeconomic and environmental drivers of pandemics, including ecosystem conversion, meat consumption, urbanization, and connectivity among cities and countries. This paper reviews how these four systemic drivers help explain the dynamics of the COVID-19 pandemic and other recent emerging infectious diseases, and the policies that can be adopted to mitigate their risks. Land-use change and meat consumption increase the likelihood of pathogen spillover from animals to people. The risk that such zoonotic outbreaks will then spread to become pandemics is magnified by growing urban populations and the networks of trade and travel within and among countries. Zoonotic spillover can be mitigated through habitat protection and restrictions on the wildlife trade. Containing infectious disease spread requires a high degree of coordination among institutions across geographic jurisdictions and economic sectors, all backed by international investment and cooperation.
Keywords: Biodiversity conservation; COVID-19; Emerging infectious diseases; Global health; Pandemics; Wildlife trade.
Figures
Similar articles
- Implications of Zoonoses From Hunting and Use of Wildlife in North American Arctic and Boreal Biomes: Pandemic Potential, Monitoring, and Mitigation.Front Public Health. 2021 May 5;9:627654. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.627654. eCollection 2021.Front Public Health. 2021.PMID: 34026707Free PMC article.Review.
- Challenges in modelling the dynamics of infectious diseases at the wildlife-human interface.Epidemics. 2021 Dec;37:100523. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2021.100523. Epub 2021 Nov 19.Epidemics. 2021.PMID: 34856500Free PMC article.Review.
- The COVID-19 pandemic is intricately linked to biodiversity loss and ecosystem health.Lancet Planet Health. 2021 Nov;5(11):e840-e850. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00258-8.Lancet Planet Health. 2021.PMID: 34774124Free PMC article.Review.
- Tropical peatlands and their conservation are important in the context of COVID-19 and potential future (zoonotic) disease pandemics.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 17;8:e10283. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10283. eCollection 2020.PeerJ. 2020.PMID: 33240628Free PMC article.
- Pandemic origins and a One Health approach to preparedness and prevention: Solutions based on SARS-CoV-2 and other RNA viruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 18;119(42):e2202871119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202871119. Epub 2022 Oct 10.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022.PMID: 36215506Free PMC article.Review.
Cited by
- The COVID-19 pandemic, an environmental neurology perspective.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022 Jun;178(6):499-511. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2022.02.455. Epub 2022 Mar 22.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022.PMID: 35568518Free PMC article.Review.
- China's Public Health Policies in Response to COVID-19: From an "Authoritarian" Perspective.Front Public Health. 2021 Dec 15;9:756677. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.756677. eCollection 2021.Front Public Health. 2021.PMID: 34976920Free PMC article.
- The ecology of COVID-19 and related environmental and sustainability issues.Ambio. 2022 Apr;51(4):1014-1021. doi: 10.1007/s13280-021-01603-0. Epub 2021 Jul 19.Ambio. 2022.PMID: 34279809Free PMC article.
- Exploring scenarios for the food system-zoonotic risk interface.Lancet Planet Health. 2023 Apr;7(4):e329-e335. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(23)00007-4.Lancet Planet Health. 2023.PMID: 37019573Free PMC article.Review.
- Strengthening preparedness against global health threats: A paradigm shift based on One Health approaches.One Health. 2022 May 7;14:100396. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2022.100396. eCollection 2022 Jun.One Health. 2022.PMID: 35686149Free PMC article.
References
- Armelagos GJ, Brown PJ, Turner B. Evolutionary, historical and political economic perspectives on health and disease. Social Science and Medicine. 2005;61:755–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

