Abstract
The implementation of preparedness strategies to prevent and mitigate the impact of global health threats poses several challenges. It should promptly identify cross-cutting drivers of pandemic threats, assess context-specific risks, engage multiple stakeholders, and translate complex data from multiple sources into accessible information for action. This requires a coordinated, multidisciplinary and multisectoral effort engaging systems that, most of the time, work in isolation.
The One Health (OH) approach promotes the collaboration and communication among different disciplines and sectors, and could be applied across the preparedness phases at national and international level.
We discuss here gaps and needs in preparedness strategies, which can benefit from the OH approach, and a set of actionable recommendations, as shared with the G20–2021 with a dedicated Policy Brief.
The discussion adds to the current debate about OH operationalization and promotes a paradigm shift towards coordinated prevention and preparedness strategies for early assessment and management of global health threats.
Keywords: One Health, Prevention, Preparedness, Emerging infectious diseases
1. Introduction
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for the dramatic COVID-19 pandemic [1,2], shows clearly that global health threats are due to multifarious causes, complex determinants and drivers. Moreover, the impact caused by the pandemic is said to be syndemic, since it involves a multitude of factors (such as socio-economic, cultural and environmental) affecting communities on a global scale [[3], [4], [5]].
The evidence that emerges strongly suggests the need to develop and implement multidisciplinary, multi-sector and multi-actor preparedness strategies to address this complexity and reduce fragmentation of strategies in the implementation of procedures and plans required to anticipate and contain a health emergency [6].
The zoonotic origin of most emerging pathogens and the crucial role played by humans in the over-exploitation of the environment, suggest intercepting possible drivers of global health threats at the human-animal-environmental interface and reducing their possible impact with strong prevention actions. The identification of drivers of potential threats before they affect societies requires assessing context-specific risks with the support of multiple stakeholders, and translating complex data from multiple sources into accessible information for action [7].
To support this aim the One Health approach, as defined by the WHO, represents a valid scientific strategy “to designing and implementing programmes, policies, legislation and research in which multiple sectors communicate and work together to achieve better public health outcomes” [8].
Adopting and integrating the OH approach into plans and policies, both at national and international level, requires a radical change of strategy in terms of governance, capacity building, training and research to overcome the current fragmentation and barriers and to allow the required interaction, collaboration and coordination across sectors and disciplines.
The Group of Twenty (G20) is the international forum that brings together the world's major economies. The forum has met every year since 1999 and the G20_2021 thematic was focused on People-Planet-Prosperity [9].
The Think20 (T20) is the official engagement group of the G20, bringing together leading think-tanks and research centers worldwide. It serves as the ‘ideas bank’ of the G20 and aims at providing research-based policy recommendations to the G20 leaders [10].
With the aim of providing concrete recommendations to the G20_2021 to enhance the integration of the OH approaches in preparedness strategies, we delivered through the T20 the Policy Brief (PB) titled “One health-based conceptual frameworks for comprehensive and coordinated prevention and preparedness plans addressing global health threats” [11].
We discuss here the evidence reported in the PB on the unmet strategic needs that are presently hampering the implementation of efficient pandemic preparedness strategies and how these could be addressed through a OH approach.
2. Rationale for integrating one health approaches in preparedness strategies
WHO defines emergency preparedness as “the knowledge and capacities and organizational systems developed by governments, response and recovery organizations, communities and individuals to effectively anticipate, respond to, and recover from the impact of likely, imminent, emerging, or current emergencies” [12].
The One Health High Level Expert Panel established in 2021, defines OH as “…. An approach (which) mobilizes multiple sectors, disciplines and communities at varying levels of society to work together to foster well-being and tackle threats to health and ecosystems, while addressing the collective need for clean water, energy and air, safe and nutritious food, taking action on climate change, and contributing to sustainable development” [13].
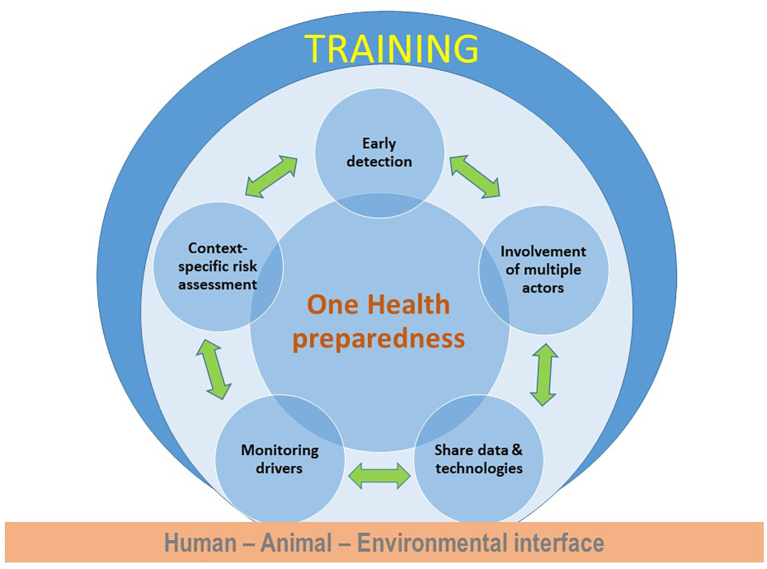
The integration of OH approaches in preparedness strategies could support the consolidation of those preparedness pillars (Fig. 1) which rely on the coordinated action of multiple sectors and disciplines [14,15].
Fig. 1.
Pillars of preparedness enhanced by multisectorial & multidisciplinary approaches at the human-animal-environment interface.
2.1. Early detection of health threats
Health threats refer to events and situations which can cause or threaten to cause a public health emergency with serious and lasting impact on the public health and/or other aspects of human and animal wellbeing and their environment. Health threats like outbreaks of infectious agents have a cumulative societal cost that can be reduced by the early detection of possible threats [16,17].
Although the concept of anticipating possible threats has for a long time been an integral part of the definition of preparedness, the strategies developed showed that preparedness is mainly intended as a means to make the response to threats more efficient. This, however, underestimates its equally fundamental role in triggering more timely actions aimed at preventing or, should this not be possible, detecting possible warning signals earlier on [7,12,18,19].
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how preparedness strategies failed to consider all the necessary elements to counter this evolving health threat [20,21].
Prevention and preparedness strategies should consider the benefit of relying on integrated surveillance and OH risk-based approaches for key public health risks associated with emerging zoonoses and other threats. [22].
2.2. Monitoring multiple and interconnected drivers
The concept of drivers is used in different fields, including economics, social sciences, technology, health and environmental sciences. Drivers are defined as issues that shape the development of a society, organization, industry, research area, technology, etc. They may act as facilitators or modifiers of effect on the onset of emerging risks. Namely, drivers can either amplify or attenuate the magnitude or frequency of risks arising from various sources [23].
Many of the upstream drivers of health threats, whether the potential threat is a zoonosis, a neglected tropical disease or antimicrobial resistance (AMR) [[24], [25], [26], [27]] lie outside the human health sector (e.g. animal health, land use, loss of biodiversity, climate change, urbanisation, conflicts) and are multifactorial.
In many cases drivers can produce signals that could be assessed and monitored to anticipate threat emergence, to strengthen public health intelligence [28]. Understanding and addressing these threats requires the establishment of a comprehensive detection system with specific inter-sectorial data collection and analysis, allowing context specific risk analysis with ad hoc metrics and multisectoral indicators [29].
2.3. Ensuring prompt access and sharing of information, data and technologies transparently
Systematically collecting integrated data and information at the human-animal-environment interface should be followed by the effective access and use of data by all the relevant stakeholders as a critical building block of national preparedness [30,31].
Although the WHO recognises that the International Health Regulations (IHR) have improved the detection of threats and the sharing of information [21], the COVID-19 pandemic showed us that further efforts are needed. A recent European Commission Communication [32], has highlighted that effective data sharing for coordinated analysis is also hampered by the crucial lack of indicators to detect and respond to new infectious diseases of unknown origins.
Integrated multisectoral databases based on OH approach are being recommended in the international relevant guidance for zoonosis and AMR prevention and preparedness plans [33,34].
Integrated risk assessment, implemented with the concomitant participation of all the relevant sectors involved in the surveillance of a given threats, are recommended to enhancing cross-sectoral collaboration and improving data collection and data-sharing across different sectors [35,36].
2.4. Considering the multiplicity of the actors, stakeholders, disciplines and related interests involved
To ensure the establishment of a sustainable OH preparedness system aimed at addressing global health threats a “whole of society” vision is fundamental [29,37]. As per WHO definition “whole of government and whole of society approaches are grounded in strategies that enhance joined-up government, improved coordination and the integration and diffusion of responsibility for health throughout government and society.” [38].
However, tools for active and comprehensive stakeholder engagement need to be refined and tested considering also the conflicting interests that may arise. This point is exemplified by the implementation of biosecurity measures in live animal markets or intensive animal farms, where drastic measures (such as closing markets, increasing in the spacing between animals in farms) might lead to a loss of income for vendors and small-scale famers [17,39]. A delicate balance will need to be found between the need to reach consensus among the involved stakeholders and formulate sustainable strategies.
2.5. Enhancing local sustainability and contrasting exacerbation of social inequalities
Prevention and preparedness strategies should be sustainable and aimed at contrasting exacerbation of social and health inequalities also relying on community engagement [40,41]. Implemented actions should be calibrated to the local system with context-specific risk assessment and include capacity building when required (e.g. strengthening of weak surveillance systems or social and economic protection for those who need to convert to new income activities) to reduce the impact on the services and communities in case of any threat [42,43].
3. Actionable recommendations
Adopting and implementing OH approaches in prevention and preparedness strategies have been consistently advocated on the basis of its strategic benefits considering that the emergence of infectious diseases and pandemic threats is influenced by multiple factors (including behavioural, environmental, social and economic ones) and that OH could address all these factors thanks to its multidisciplinary approach [16,19,[44], [45], [46], [47], [48], [49]].
In order to enhance the operationalization of OH preparedness strategies we suggest here two key areas that need to be addressed to facilitate and accelerate this process.
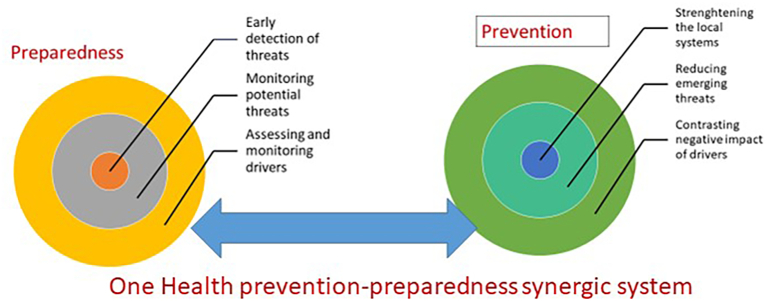
The first area refers to the mainstreaming of OH approaches in preparedness and prevention plans, making OH an integral part of the national, regional and international strategy aimed at countering the evolving of potential threats to global health rather than a distinct One Health action plan addressing specific sectors like zoonosis or AMR [37,50]. We propose the implementation of a One Health-based Conceptual Framework to promote the integration of OH with identified priorities for action (Appendix 2 in [11]). On the basis of specific indicators, the national surveillance system should identify local potential drivers for possible threats to health and monitor them. As discussed, these drivers may involve various sectors beside health and therefore a multidisciplinary and multisectorial surveillance system should be considered. The information and data collected, analysed with a One Health approach, support the elaboration and updating of prevention and preparedness plans and provide evidence for appropriate decisions and related actions (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
One Health prevention-preparedness synergic system.
The need of assessing the risk of drivers potentially involved in the development of threats and of promptly detecting threats of unknown origins, should motivate the identification of metrics and indicators which allow the multidisciplinary of the OH approach being operational, monitored and evaluated.
The conclusions of FAO's evaluation of the largest animal health programme in the world on zoonotic diseases and AMR using OH approach, stress the need of setting a One Health Sustainable Development Goal because the lack of such indicators may reduce national commitment to the implementation of One Health [51].
The second area in need of proper action involves governance, operational research, and capacity building to cope with barriers and obstacles which are hampering OH integration.
In line with these needs, we identified specific recommendations which were provided to the G20–2021 with the PB titled “One health-based conceptual frameworks for comprehensive and coordinated prevention and preparedness plans addressing global health threats” [11].
We recommended to the international bodies guidance for specific governance structure across sectors and disciplines at national and international level, to ensure harmonised institutionalisation of One Health strategies (including guidance for setting means for integrated data collection and analysis, risk assessment, and resource allocation).
We recommended also the development, in coordination with the countries that are already implementing One Health strategies, of a cost-effectiveness evaluation framework, with modular options to tailor for local conditions. Ad-hoc operational research, to assess and quantify the added value and sustainability of One Health strategies in the fields of prevention and preparedness should also be considered.
Finally, we stress the urgency to motivate the national governments to devote adequate resources to the development and implementation of trainings on prevention and preparedness with multidisciplinary and multisectoral approaches to enhance awareness of benefits of sharing data and information and capacity of analysing complex set of data to take appropriate actions [52].
4. Conclusions
We are required to make important and urgent decisions on complex situations, and we need to base them on a comprehensive analysis of data and information from multiple areas and sectors that might be relevant to decision-making. OH interoperable databases and data democratization platforms can facilitate the sharing of required information and should be considered as integral part of the proposed prevention-preparedness synergic system. This could also enhance IHR implementation and could therefore be included in the emerging idea of a Pandemic Treaty [53,54].
Sharing with the relevant stakeholders the identified risks for potential pandemics, or other global health threats, facilitates their participation to the dynamic cycle of protecting the environment through a sustainable behaviour, decreasing the risk of potential new threats, and supporting identification of possible drivers of pandemic. In addition, this process will keep all the stakeholders involved informed, active and resilient in case of emergency.
Addressing global health threats through a lens that highlights the complexity of the involved system is what leads to identifying in OH as a viable framework to support global health strategies. Given the wide range of determinants of emergence and impact that operate within globalized yet local contexts, no convenient blueprints can be put on the table to counter current and future global health threats. Rather, local custom-made solutions will need to be found through the engagement and consensus of multiple actors. The T20 final communiqué to G20–2021 [55], the Declaration of the G20 Health Ministers [56] and the G20 Health and Finance Ministers communiqué [57] have considered the recommendations provided with the PB [11]. We hope that this can contribute to further the current debate about OH strategies operationalisation, lead to concrete actions capable of transforming the current OH momentum into long-term commitments and promote paradigmatic shifts in prevailing thinking around preparedness that can translate in more effective global and local strategies supported by equitable sharing of innovation, prevention and response focused technologies.
OH preparedness can enhance our understanding of risk factors of complex global health threats at the human-animal-environment interface. It can also prove a new point of view from which we can hypothesize future potential scenarios and adapt national and regional prevention and preparedness strategies, to counteract the current megatrends that are damaging our entire planet [46,[58], [59], [60], [61]].
Funding
ISS research 2020-22_ ISS20-d955b07fd1e4
Declaration of Competing Interest
None
References
- 1.Our word in data Total confirmed COVID-19 deaths. 2022. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/covid-deaths-income?country=Low+income~Lower+middle+income~High+income~Upper+middle+income (Accessed January 31, 2022)
- 2.IMF (International Monetary Fund) Transcript of the World Economic Outlook update press briefing. 2021. https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2021/01/28/tr012621-transcript-of-the-world-economic-outlook-update-press-briefing (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 3.Horton R. Offline: COVID-19 is not a pandemic. Lancet. 2020;396(10255):874. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32000-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kenyon C. Syndemic responses to COVID-19 should include an ecological dimension. Lancet. 2020;396(10264):1730–1731. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32219-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hadi E., Jalili M. The role of environmental factors to transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) AMB Express. 2020:10. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01028-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Global Preparedness Monitoring Board (GPMB) A World Prepared: Global Preparedness Monitoring Board Strategic Plan 2021–2023. https://www.gpmb.org/annual-reports/overview/item/gpmb-strategic-plan-2021-2023
- 7.Daszak P., Amuasi J., das Neves C.G., et al. IPBES secretariat; Bonn, Germany: 2020. Workshop Report on Biodiversity and Pandemics of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. (accessed December 10, 2021) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe. One Health. https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-policy/one-health (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 9.https://www.mef.gov.it/en/focus/People-planet-prosperity-The-Italian-G20-Finance-track-00001/ (Accessed February 25, 2022)
- 10.https://www.ispionline.it/it/think-t20-italy (Accessed February 25, 2022)
- 11.Agrimi U., Carere M., Cubadda F., et al. T20 Policy Brief on “One Health-Based Conceptual Frameworks for Comprehensive and Coordinated Prevention and Preparedness Plans Addressing Global Health Threats”. 2021. https://www.t20italy.org/2021/09/08/one-health-based-conceptual-frameworks-for-comprehensive-and-coordinated-prevention-and-preparedness-plans-addressing-global-health-threats/
- 12.World Health Organization A Strategic Framework for Emergency Preparedness. 2016. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/a-strategic-framework-for-emergency-preparedness Geneva.
- 13.One Health High Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP)-2021. https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/statements/joint-tripartite-and-unep-statement-definition-one-health#:~:text=The%20One%20Health%20definition%20developed,of%20people%2C%20animals%20and%20ecosystems (Accessed January 31, 2022)
- 14.WHO Multisectoral Preparedness Coordination Framework: Best Practices, Case Studies and Key Elements of Advancing Multisectoral Coordination for Health Emergency Preparedness and Health Security. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 15.National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine . The National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2022. Systematizing the One Health Approach in Preparedness and Response Efforts for Infectious Disease Outbreaks: Proceedings of a Workshop. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.World Bank People Pathogens and our Planet: Volume 2: The Economics of One Health (Report no. 69145-GLB) 2012. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/11892 Washington, DC. (Accessed January 31, 2022)
- 17.Zinsstag J., Utzinger J., Probst-Hensch N., et al. Towards integrated surveillance-response systems for the prevention of future pandemics. Infect. Dis. Poverty. 2020;9:140. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00757-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.OCHA website What Is Preparedness? 2021. https://www.humanitarianresponse.info/en/coordination/preparedness/what-preparedness (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 19.Nelson C., Lurie N., Wasserman J., et al. Conceptualizing and defining public health emergency preparedness. Am. J. Public Health. 2007;97(Suppl. 1):S9–S11. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2007.114496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.The Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response for the WHO Executive Board . 2021. Second Report on Progress by the Independent Panel for Pandemic Preparedness and Response for the WHO Executive Board. (Accessed December 10, 2021) [Google Scholar]
- 21.World Health Organization Action plan to improve public health preparedness and response in the WHO European Region 2018–2023. 2019. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/312235/9789289053914-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y Copenhagen. (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 22.Consultative Group for International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) Responding To Covid-19: Cgiar's Contribution To Global Response, Recovery And Resilience 2022. https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/108548
- 23.Richardson J., Lockhart C., Pongolini S., et al. Drivers for emerging issues in animal and plant health. EFSA J. 2016:14(S1). doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2016.s0512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu T. The socioeconomic and environmental drivers of the COVID-19 pandemic: a review. Ambio. 2021;50(4):822–833. doi: 10.1007/s13280-020-01497-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Durrance-Bagale A., Rudge J.W., Singh N.B., et al. Drivers of zoonotic disease risk in the Indian subcontinent: a scoping review. One Health. 2021;13 doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cole J., Desphande J. Poultry farming, climate change, and drivers of antimicrobial resistance in India. Lancet Planetary Health. 2019;3(12):e494–e495. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(19)30236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.World Health Organization . Draft For Public Consultation; Geneve: 2021. Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals One Health Companion Document to the Neglected Tropical Diseases Road Map 2021–2030.https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/ntds/rabies/online-public-consultation.-one-health-companion-document/draft-for-public-consultation-one-health-companion-document-for-ntd-road-map.pdf?sfvrsn=62d19e34_22&download=true (Accessed December 10, 2021) [Google Scholar]
- 28.Olson S.H., Benedum C.M., Mekaru S.R., et al. Drivers of emerging infectious disease events as a framework for digital detection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015;21(8) doi: 10.3201/eid2108.141156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Machalaba C.C., Salerno R.H., Behravesh C.B., et al. Institutionalizing One Health: from assessment to action. Health Security. 2018;16(S1) doi: 10.1089/hs.2018.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khan M.S., Osman D., Ngozi A.E., et al. Using critical information to strengthen pandemic preparedness: the role of national public health agencies. BMJ Glob. Health. 2020;5(9) doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Naguib M.M., Ellström P., Järhult J.D., et al. Towards pandemic preparedness beyond COVID-19. Lancet Microbe. 2020;1(5):e185–e186. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30088-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.European Commission Drawing the Early Lessons from the COVID-19 Pandemic. 2021. https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/communication150621.pdf Brussels. (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 33.World Health Organization (WHO) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE)Taking a Multisectoral, One Health Approach: A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries. 2019. https://extranet.who.int/sph/sites/default/files/document-library/document/English.pdf
- 34.WHO Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2015. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509763
- 35.Dente M.G., Riccardo F., Van Bortel W., et al. Enhancing preparedness for arbovirus infections with a one health approach: the development and implementation of multisectoral risk assessment exercises. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020;2020:4832360. doi: 10.1155/2020/4832360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tripartite organisations (FAO, OIE and WHO) The Operational Tool on Joint Risk Assessment (JRA OT) https://www.who.int/news/item/17-12-2020-launch-of-the-tripartite-joint-risk-assessment-operational-tool
- 37.Flowra M.T., Asaduzzaman M. Resurgence of infectious diseases due to forced migration: is planetary health and One Health action synergistic? Lancet Planet Health. 2018;2(10):e419–e420. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(18)30203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe. Governance for Health in the 21st Century. 2011. https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/154252/Health-2020-Conf.-Governance-for-health-....pdf Baku.
- 39.Zahouli J.B.Z., Koudou B.G., Müller P., et al. Effect of land-use changes on the abundance, distribution, and host-seeking behavior of Aedes arbovirus vectors in oil palm-dominated landscapes, southeastern Côte d’Ivoire. PLoS One. 2017;12(12) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.World Health Organization A World in Disorder: Global Preparedness Monitoring Board Annual Report. 2020. https://apps.who.int/gpmb/assets/annual_report/2020/GPMB_2020_AR_EN_WEB.pdf Geneva. (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 41.Alberti P.M., Lantz P.M., Wilkins C.H. Equitable pandemic preparedness and rapid response: lessons from COVID-19 for pandemic health equity. J. Health Polit. Policy Law. 2020;45(6):921–935. doi: 10.1215/03616878-8641469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Economists at Large, Campbell R, Knowles T. The Economic Impacts of Losing Livestock in a Disaster. 2011. https://www.gndr.org/images/newsite/Learning/Animal-Protection/Ecolarge-LivestockDisasterEconomics Melbourne.
- 43.Gongal G., Ofrin R.H. Animal welfare, One Health and emergency preparedness and response in the Asia-Pacific region. WHO South-East Asia Journal of Public Health. 2020;9:50–51. doi: 10.4103/2224-3151.282996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.FAO Protecting People and Animals from Disease Threats. 2019. http://www.fao.org/emergencies/resources/documents/resources-detail/en/c/1105803/ Rome.
- 45.United Nations Environment Programme and International Livestock Research Institute . Nairobi; 2020. Preventing the Next Pandemic: Zoonotic Diseases and how to Break the Chain of Transmission.https://www.ilri.org/publications/preventing-next-pandemic-zoonotic-diseases-and-how-break-chain-transmission (Accessed December 10, 2021) [Google Scholar]
- 46.Plowright R.K., Reaser J.K., Locke H., et al. Land use-induced spillover: a call to action to safeguard environmental, animal, and human health. Lancet Planet Health. 2021;5(4):e237–e245. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00031-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.World Organisation for Animal Health COVID-19. https://www.oie.int/en/what-we-offer/emergency-and-resilience/covid-19/ (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 48.Larsen H.D., Fonager J., Lomholt F.K., et al. Preliminary report of an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in mink and mink farmers associated with community spread, Denmark, June to November 2020. Euro Surveill. 2021;26(5) doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210009. pii=2100009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.World Health Organization SARS-CoV-2 in animals used for fur farming: GLEWS+ risk assessment. 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/339626?locale-attribute=en& Geneve. (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 50.McKee M. Drawing light from the pandemic: a new strategy for health and sustainable development—a review of the evidence. 2021. https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-policy/european-programme-of-work/pan-european-commission-on-health-and-sustainable-development/publications/evidence-review.-drawing-light-from-the-pandemic-a-new-strategy-for-health-and-sustainable-development.-2021 Copenhagen. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.FAO One Health approach in FAO's work on zoonoses and Antimicrobial resistance. Hundred and Thirtieth Session 22-26 March 2021. 2021. https://www.fao.org/3/ne861en/ne861en.pdf Rome.
- 52.Chan Fung M.F. Overcoming complacency in the face of infectious disease. Nat. Med. 2021;27:363. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01259-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Monti M., Torbica A., Mossialos E., et al. A new strategy for health and sustainable development in the light of the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2021;398(10305):1029–1031. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01995-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ruckert Arne, das Neves Carlos Gonçalo, Amuasi John, et al. One Health as a pillar for a transformative pandemic treaty. https://www.graduateinstitute.ch/sites/internet/files/2021-11/policybrief-onehealth-v3.pdf
- 55.T20 Italy 2021 final communiqué. 2021. https://www.t20italy.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/T20-Italy-Final-Communique.pdf Rome. (Accessed December 10, 2021)
- 56.G20 Italy Declaration of the G20 Health Ministers. 2021. https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pagineAree_5459_8_file.pdf Rome 5–6 September 2021. Rome.
- 57.G20 Italy Joint G20 Finance and Health Ministers Meeting. 2021. https://www.g20.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/G20-Joint-Finance-and-Health-Ministers-Communique-29-October-2021.pdf Communiqué. Rome.
- 58.de Garine-Wichatitsky M., Binot A., Morand S., et al. Will the COVID-19 crisis trigger a one health coming-of-age? Lancet Planet Health. 2020;4(9):e377–e378. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30179-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Waugh C., Lam S.S., Sonne C. One Health or Planetary Health for pandemic prevention? Lancet. 2020;396(10266):1882. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32387-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Amuasi J.H., Walzer C., Heymann D., et al. Calling for a COVID-19 One Health research coalition. Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1543–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31028-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Vineis P., Salmaso S. The origin of Sars-CoV-2: why it matters. Front. Public Health. 2021;9 doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.719914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]