| jupyter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Plotly's Python library is free and open source! Get started by downloading the client and reading the primer.
You can set up Plotly to work in online or offline mode, or in jupyter notebooks.
We also have a quick-reference cheatsheet (new!) to help you get started!
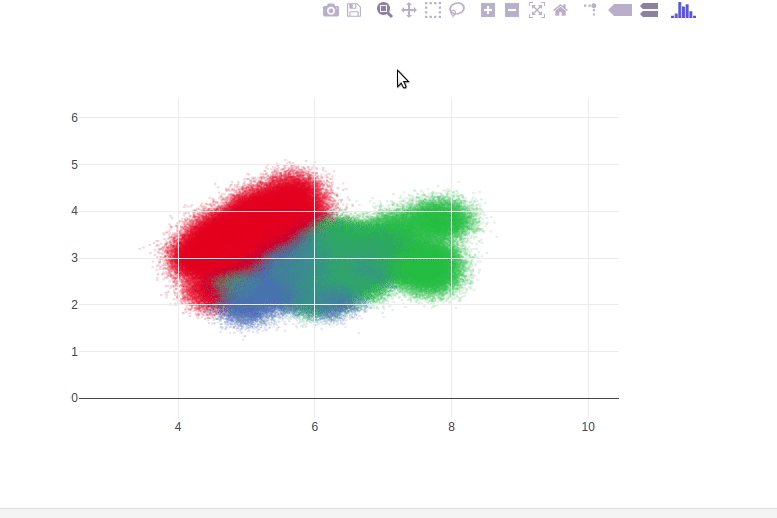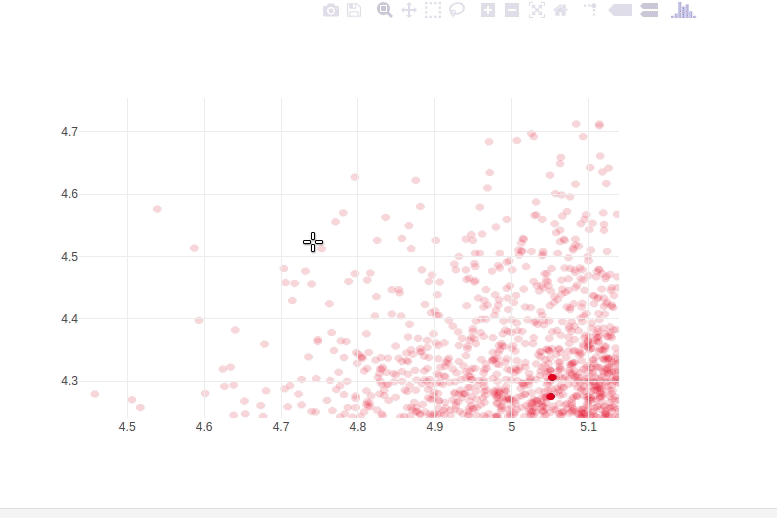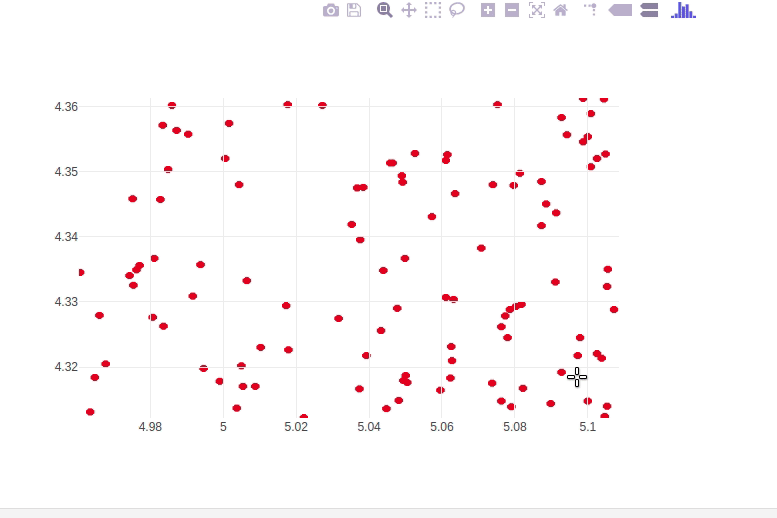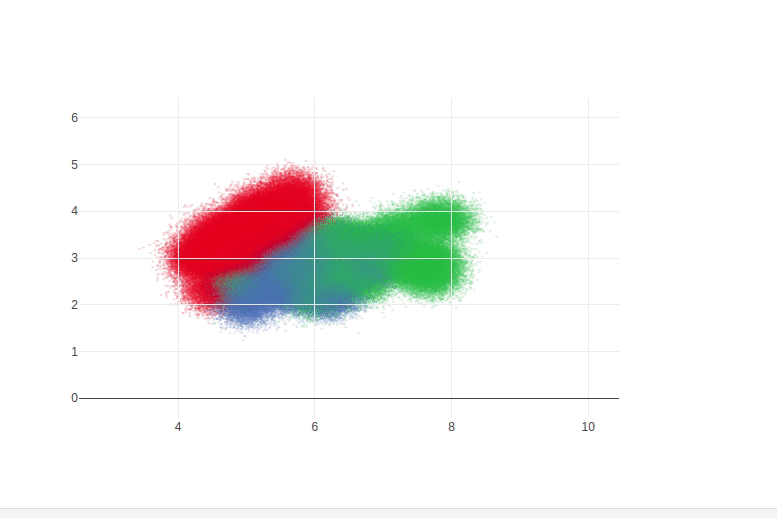
This notebook demonstrates how to use DataShader to display large datasets inside a plotly FigureWidget. Change callbacks are used to recompute the datashader image whenever the axis range or figure size changes
# coreimportioimportbase64importtime# pandasimportpandasaspd# numpyimportnumpyasnp# scikit learnfromsklearnimportdatasets# datashaderimportdatashaderasdsimportdatashader.transfer_functionsastffromdatashader.colorsimportinfernoWe will create a large dataset by duplicating the Iris dataset many times with random noise
num_copies=7000# 1,050,000 rowsiris_data=datasets.load_iris() feature_names= [name.replace(' (cm)', '').replace(' ', '_') fornameiniris_data.feature_names] iris_df_orig=pd.DataFrame(iris_data.data, columns=feature_names) target_orig=iris_data.target+1# frame of featuresiris_df=pd.concat( np.random.normal(scale=0.2, size=iris_df_orig.shape) +iris_df_origforiinrange(num_copies) ).reset_index(drop=True) # array of targetstarget= [tforiinrange(num_copies) fortintarget_orig] # dataframe that includes target as categoricaliris_target_df=pd.concat([iris_df, pd.Series(target, name='target', dtype='category')], axis=1) iris_df.describe()Define a function that inputs an x/y ranges and the plot width/height and generates a DataShader image of the dataset. The image will be returned as a PIL image object
defgen_ds_image(x_range, y_range, plot_width, plot_height): ifx_rangeisNoneory_rangeisNoneorplot_widthisNoneorplot_heightisNone: returnNonecvs=ds.Canvas(x_range=x_range, y_range=y_range, plot_height=plot_height, plot_width=plot_width) agg_scatter=cvs.points(iris_target_df, 'sepal_length', 'sepal_width', ds.count_cat('target')) img=tf.shade(agg_scatter) img=tf.dynspread(img, threshold=0.95, max_px=5, shape='circle') returnimg.to_pil()x_range=[3, 10] y_range=[0, 6] plot_height=500plot_width=700# Test image generation function and display the PIL imageinitial_img=gen_ds_image(x_range, y_range, plot_width, plot_height)initial_imgimportplotly.graph_objsasgof=go.FigureWidget(data=[{'x': x_range, 'y': y_range, 'mode': 'markers', 'marker': {'opacity': 0}}], # invisible trace to init axes and to support autoresizelayout={'width': plot_width, 'height': plot_height}) f# Set background imagef.layout.images= [go.layout.Image( source=initial_img, # plotly now performs auto conversion of PIL image to png data URIxref="x", yref="y", x=x_range[0], y=y_range[1], sizex=x_range[1] -x_range[0], sizey=y_range[1] -y_range[0], sizing="stretch", layer="below")]defupdate_ds_image(layout, x_range, y_range, plot_width, plot_height): img=f.layout.images[0] # Update with batch_update so all updates happen simultaneouslywithf.batch_update(): img.x=x_range[0] img.y=y_range[1] img.sizex=x_range[1] -x_range[0] img.sizey=y_range[1] -y_range[0] img.source=gen_ds_image(x_range, y_range, plot_width, plot_height) # Install callback to run exactly once if one or more of the following properties changes# - xaxis range# - yaxis range# - figure width# - figure heightf.layout.on_change(update_ds_image, 'xaxis.range', 'yaxis.range', 'width', 'height')f.layout.dragmode='zoom'fSee these Jupyter notebooks for even more FigureWidget examples.
fromIPython.displayimportdisplay, HTMLdisplay(HTML('<link href="//fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:600,400,300,200|Inconsolata|Ubuntu+Mono:400,700" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />')) display(HTML('<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://help.plot.ly/documentation/all_static/css/ipython-notebook-custom.css">')) ! pipinstallgit+https://github.com/plotly/publisher.git--upgradeimportpublisherpublisher.publish( 'change-callbacks-datashader.ipynb', 'python/change-callbacks-datashader/', 'FigureWidget | plotly', 'Display Large Datasets with DataShader and Change Callbacks', title='DataShader Case Study', name='DataShader Case Study', uses_plotly_offline=True, has_thumbnail='true', thumbnail='thumbnail/ipython_widgets.jpg', language='python', page_type='example_index', display_as='chart_events', order=24, ipynb='~notebook_demo/239')