- Author: HuiFer
- Description: 该文介绍 mybatis 反射相关类的源码
- 源码阅读工程: SourceHot-Mybatis
- mybatis 的反射相关内容在
org.apache.ibatis.reflection下存放. 本片主要讲解org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector类, 先看一下该类的属性
publicclassReflector { /** * 实体类.class */privatefinalClass<?> type; /** * 可读 属性 */privatefinalString[] readablePropertyNames; /** * 可写 属性值 */privatefinalString[] writablePropertyNames; /** * set 方法列表 */privatefinalMap<String, Invoker> setMethods = newHashMap<>(); /** * get 方法列表 */privatefinalMap<String, Invoker> getMethods = newHashMap<>(); /** * set 的数据类型 */privatefinalMap<String, Class<?>> setTypes = newHashMap<>(); /** * get 的数据类型 */privatefinalMap<String, Class<?>> getTypes = newHashMap<>(); /** * 构造函数 */privateConstructor<?> defaultConstructor; /** * 缓存数据, 大写KEY */privateMap<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = newHashMap<>(); }- 构造方法, 构造方法传入一个类的字节码,在构造方法中设置相关的属性值
publicclassReflector { /** * @param clazz 待解析类的字节码 */publicReflector(Class<?> clazz) { type = clazz; // 构造方法addDefaultConstructor(clazz); // get 方法addGetMethods(clazz); // set 方法addSetMethods(clazz); // 字段值addFields(clazz); readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(newString[0]); writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(newString[0]); for (StringpropName : readablePropertyNames) { // 循环操作设置到缓存中,caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } for (StringpropName : writablePropertyNames) { caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName); } } }addDefaultConstructor方法 , 下面截图内容为 JDK8 mybatis 中 的内容
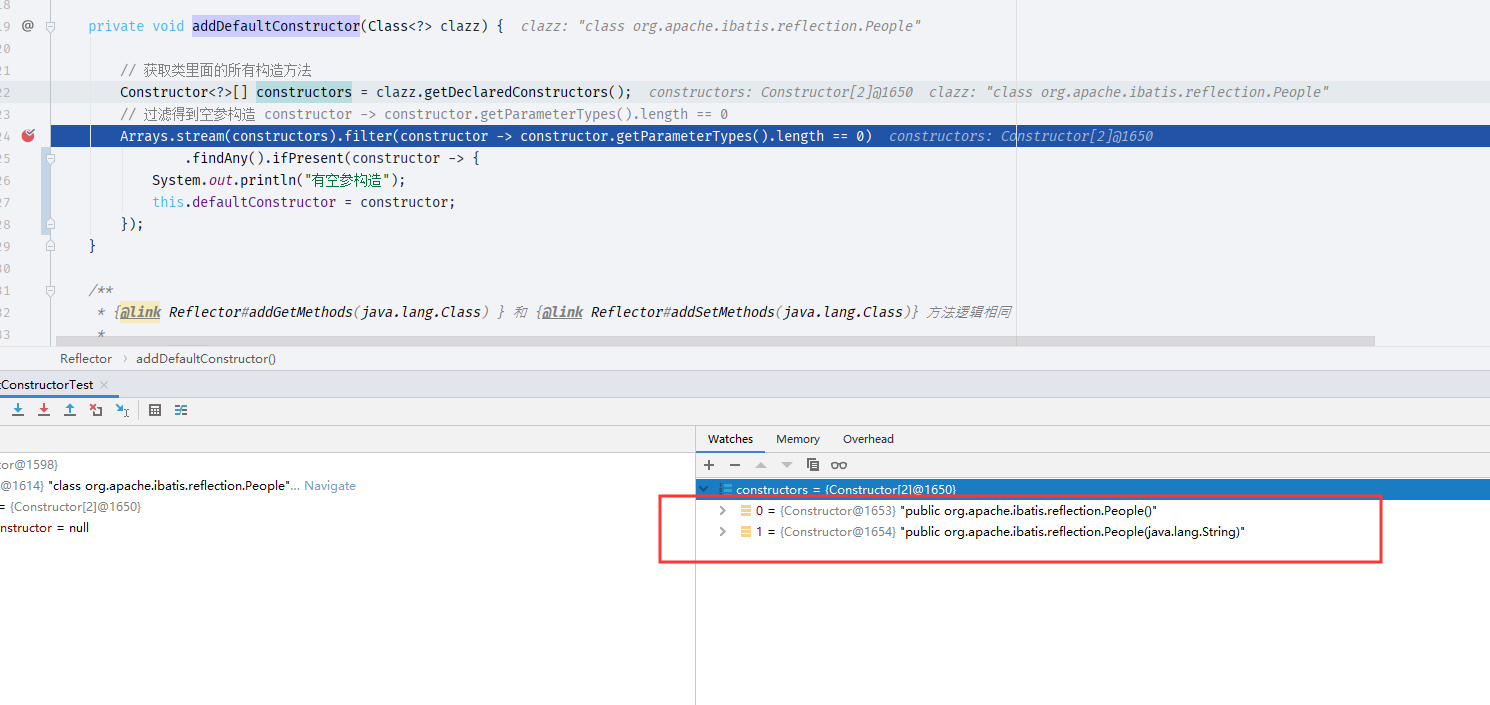
privatevoidaddDefaultConstructor(Class<?> clazz) { // 获取类里面的所有构造方法Constructor<?>[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); // 过滤得到空参构造 constructor -> constructor.getParameterTypes().length == 0Arrays.stream(constructors).filter(constructor -> constructor.getParameterTypes().length == 0) .findAny().ifPresent(constructor -> { System.out.println("有空参构造"); this.defaultConstructor = constructor; }); }- 创建一个测试类
publicclassPeople { privateStringname; publicPeople() { } publicPeople(Stringname) { this.name = name; } @OverridepublicStringtoString() { return"People{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } publicStringgetName() { returnname; } publicvoidsetName(Stringname) { this.name = name; } }importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test; importjava.lang.reflect.Constructor; classHfReflectorTest { @TestvoidgetDefaultConstructorTest() throwsException { Reflectorreflector = newReflector(People.class); // 获取空参构造方法Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = reflector.getDefaultConstructor(); Peopleo = (People) defaultConstructor.newInstance(); o.setName("hhh"); System.out.println(o); } }准备工作完成了开始进行 debug , 在
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#addDefaultConstructor这个方法上打上断点观察
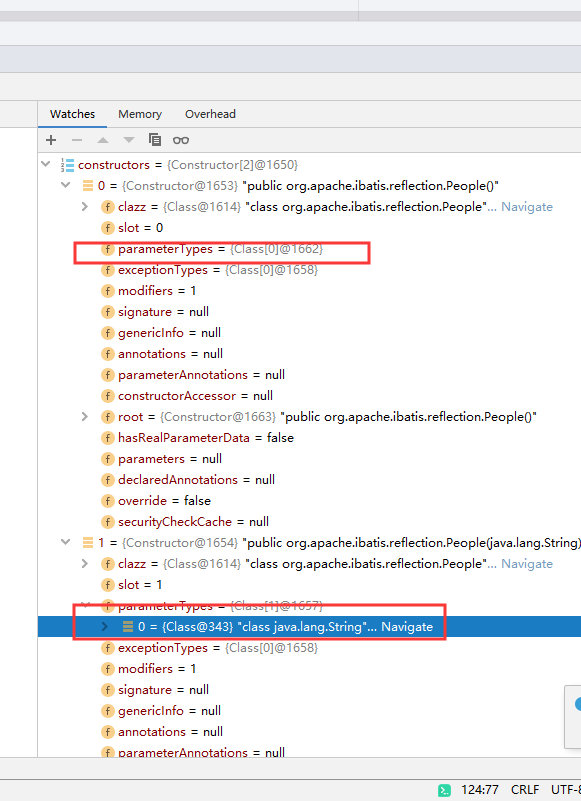
constructors属性存在两个方法,这两个方法就是我在People类中的构造方法.根据语法内容我们应该对
parameterTypes属性进行查看
可以发现空参构造的parameterTypes长度是 0.因此可以确认org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#addDefaultConstructor方法获取了空参构造
继续看
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#getDefaultConstructor方法, 该方法是获取构造函数的方法,如果构造函数没有就抛出异常,这也是为什么我们的实体类需要把空参构造写上去的原因。publicConstructor<?> getDefaultConstructor() { if (defaultConstructor != null) { returndefaultConstructor; } else { // 如果没有空参构造抛出的异常thrownewReflectionException("There is no default constructor for " + type); } }
该方法获取了所有
get和is开头的方法privatevoidaddGetMethods(Class<?> clazz) { // 反射方法Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = newHashMap<>(); Method[] methods = getClassMethods(clazz); // JDK8 filter 过滤get 开头的方法Arrays.stream(methods).filter(m -> m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName())) .forEach(m -> addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(m.getName()), m)); resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters); }
该方法中依旧使用了 JDK8 语法通过
m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName())来判断是否是get或·is开头的内容调用
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyNamerpublicstaticbooleanisGetter(Stringname) { // 在语义上 is 开头的也是get开头的return (name.startsWith("get") && name.length() > 3) || (name.startsWith("is") && name.length() > 2); }
resolveGetterConflicts方法后续介绍
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#getClassMethods,该方法将传入对象的所有可见方法都获取到进行唯一标识处理成一个Map对象 添加方法为org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#addUniqueMethodsprivateMethod[] getClassMethods(Class<?> clazz) { // 方法唯一标识: 方法Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods = newHashMap<>(); Class<?> currentClass = clazz; while (currentClass != null && currentClass != Object.class) { // getDeclaredMethods 获取 public ,private , protected 方法addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, currentClass.getDeclaredMethods()); // we also need to look for interface methods -// because the class may be abstract// 当前类是否继承别的类(实现接口)如果继承则需要进行操作Class<?>[] interfaces = currentClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) { // getMethods 获取本身和父类的 public 方法addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, anInterface.getMethods()); } // 循环往上一层一层寻找最后回到 Object 类 的上级为null 结束currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass(); } Collection<Method> methods = uniqueMethods.values(); returnmethods.toArray(newMethod[0]); }
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#addUniqueMethodsprivatevoidaddUniqueMethods(Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods, Method[] methods) { for (MethodcurrentMethod : methods) { // 桥接, 具体还不知道// TODO: 2019/12/9 JAVA 桥接方法if (!currentMethod.isBridge()) { // 方法的唯一标识Stringsignature = getSignature(currentMethod); // check to see if the method is already known// if it is known, then an extended class must have// overridden a methodif (!uniqueMethods.containsKey(signature)) { uniqueMethods.put(signature, currentMethod); } } } }
唯一标识方法
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#getSignature/** * 方法唯一标识,返回值类型#方法名称:参数列表 * * @param method * @return */privateStringgetSignature(Methodmethod) { StringBuildersb = newStringBuilder(); Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (returnType != null) { sb.append(returnType.getName()).append('#'); } sb.append(method.getName()); Class<?>[] parameters = method.getParameterTypes(); for (inti = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { sb.append(i == 0 ? ':' : ',').append(parameters[i].getName()); } returnsb.toString(); }
照旧我们进行 debug 当前方法为
toString方法从返回结果可以看到
sb.toString返回的是:返回值类型#方法名上图返回结果为
void#setName:java.lang.String命名规则:返回值类型#方法名称:参数列表回过头看看
uniqueMethods里面是什么方法签名:方法
目前完成了一部分还有一个继承问题需要 debug 看一下, 编写一个
Man继承People还需要实现接口publicclassManextendsPeopleimplementsTestManInterface { @OverridepublicIntegerinte() { return1; } publicStringhello() { return"hello"; } }
publicinterfaceTestManInterface { publicIntegerinte(); }
目标明确了就直接在
这里打断点了
在进入循环之前回率先加载本类的所有可见方法
if (!uniqueMethods.containsKey(signature)) { // 如果存在该方法唯一签名则不添加uniqueMethods.put(signature, currentMethod); }
接下来断点继续往下走
走到这一步我们来看看
currentClass.getSuperclass()是不是上一级的类通过断点可见这个
currentClass现在是People类,根据之前所说的最终uniqueMethods应该存在父类的方法可以看到父类的方法也都存在了
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#resolveGetterConflicts这个方法解决了
get方法的冲突问题,同名方法不同返回值privatevoidresolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters) { for (Entry<String, List<Method>> entry : conflictingGetters.entrySet()) { Methodwinner = null; StringpropName = entry.getKey(); booleanisAmbiguous = false; for (Methodcandidate : entry.getValue()) { if (winner == null) { winner = candidate; continue; } Class<?> winnerType = winner.getReturnType(); Class<?> candidateType = candidate.getReturnType(); if (candidateType.equals(winnerType)) { if (!boolean.class.equals(candidateType)) { isAmbiguous = true; break; } elseif (candidate.getName().startsWith("is")) { winner = candidate; } } elseif (candidateType.isAssignableFrom(winnerType)) { // OK getter type is descendant } elseif (winnerType.isAssignableFrom(candidateType)) { winner = candidate; } else { isAmbiguous = true; break; } } addGetMethod(propName, winner, isAmbiguous); } }
org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector#addFields获取类的所有字段没什么好说的直接递归就可以获取了.
private void addFields(Class<?> clazz) { Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (!setMethods.containsKey(field.getName())) { // issue #379 - removed the check for final because JDK 1.5 allows// modification of final fields through reflection (JSR-133). (JGB)// pr #16 - final static can only be set by the classloader int modifiers =field.getModifiers(); if (!(Modifier.isFinal(modifiers) &&Modifier.isStatic(modifiers))) { addSetField(field); } } if (!getMethods.containsKey(field.getName())) { addGetField(field); } } if (clazz.getSuperclass() !=null) { addFields(clazz.getSuperclass()); } }
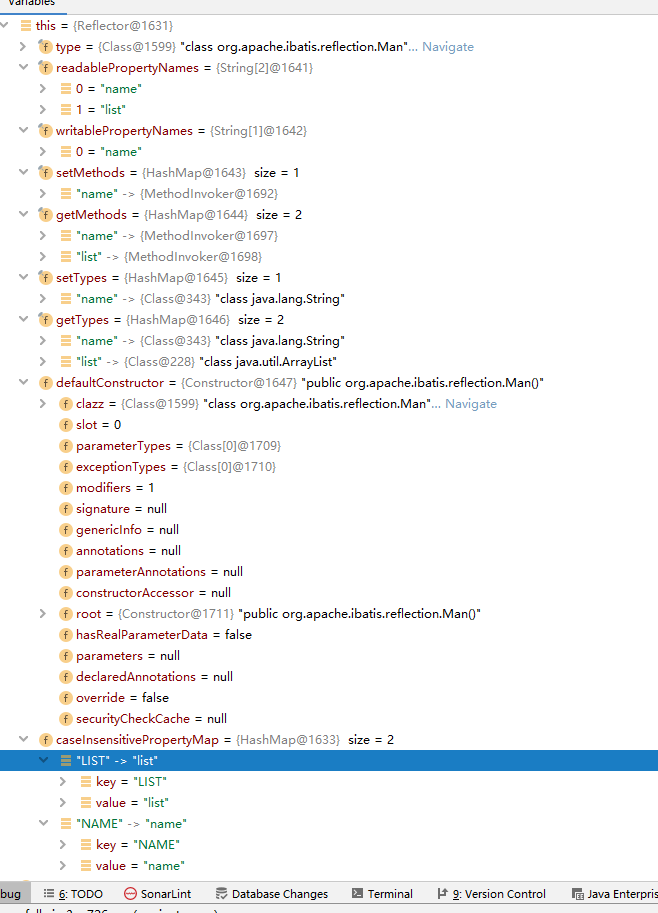
- 下图为一个类的解析结果