ArrayList 是日常开发中相当常见、面试也相当常考的一种 JDK 集合类,了解并熟悉、甚至能实现一个 ArrayList 对面试、提升自己编码功底大有益处。
这部分是 ArrayList 的简单使用技巧,主要是介绍 ArrayList 的几个常见方法。
/** * 编写一个ArrayList的简单实用demo * ArrayList 的常见方法包括: * add(element):添加元素 * get(index):获取下标元素 * remove(index):移除下标对应元素 * set(index,element):将index处的元素修改为element */publicclassarrayList { publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) { // 创建 ArrayList 的对象ArrayListal = newArrayList(); // 添加元素al.add("finky"); // 构造随机数并进行添加Randomrnd = newRandom(); for (inti = 0; i < 20; i++) { al.add(rnd.nextInt(1000)); } // 取出ArrayList里的元素进行打印for (inti = 0; i < al.size(); i++) { System.out.print(al.get(i) + " "); } // 修改0号index成的元素为doocsSystem.out.println(); al.set(0, "doocs"); System.out.println(al.get(0)); // 移除“doocs”元素al.remove(0); System.out.println(al.get(0)); } }// 这是上面打印后的demo,可以看到第0处下标元素先是修改成了doocs,进行移除后,第0处下标元素变成了912finky91292228430567556515910973298491920296397358145610190839845doocs912我们来看看 ArrayList 的源码:
// ArrayList 初始化时默认大小为10privatestaticfinalintDEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 直接初始化的话一个空数组privatestaticfinalObject[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 初始化ArrayList,传入初始化时的大小publicArrayList(intinitialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = newObject[initialCapacity]; } elseif (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } // 如果不传入大小的话就默认大小是10,那么这里就有一个问题:我们上面插入的元素超过了10,继续插入元素就会进行拷贝扩容,性能不是特别高。所以我们一般情况下初始化时给定一个比较靠谱的数组大小,避免到时候导致元素不断拷贝publicArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }总结一下 ArrayList 初始化:我们创建 ArrayList 对象时,如果没有传入对应的大小,就会默认创建一个元素大小为 10 的数组,下次插入元素超过 10 时,会进行数组的拷贝扩容,这样性能消耗太高,所以建议就是在初始化时给定一个不要太小的容量大小。==
先上add 方法的代码:
publicbooleanadd(Ee) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e; returntrue; } publicvoidadd(intindex, Eelement) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } publicvoidadd(Ee) { checkForComodification(); try { inti = cursor; ArrayList.this.add(i, e); cursor = i + 1; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsExceptionex) { thrownewConcurrentModificationException(); } } privatevoidrangeCheck(intindex) { if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) thrownewIndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } }先判断当前数组元素是否满了,如果塞满了就会进行数组扩容,随后进行数组拷贝。
再然后插入元素,同时对应的 index++。
publicEset(intindex, Eelement) { rangeCheck(index); EoldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; returnoldValue; } publicvoidset(Ee) { if (lastRet < 0) thrownewIllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsExceptionex) { thrownewConcurrentModificationException(); } }1、先进行 index 判断是否越界,如果没有越界的话获取原来的旧的值
2、进行替换并返回该位置原来的旧的值
publicEget(intindex) { rangeCheck(index); returnelementData(index); }进行 index 是否越界的判断,然后去取对应下标的值。
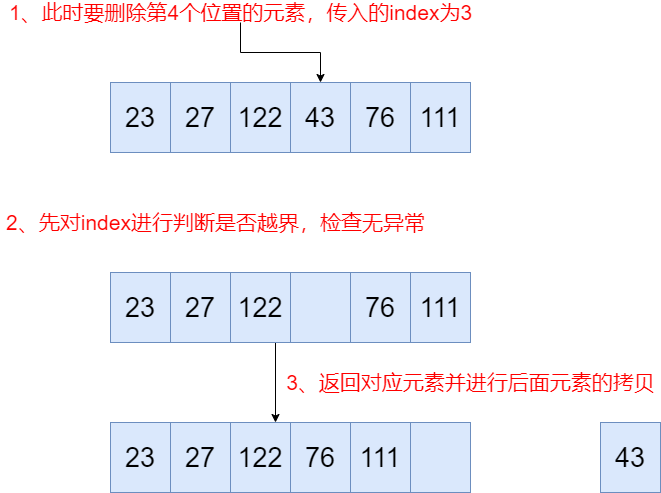
publicvoidremove() { if (lastRet < 0) thrownewIllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsExceptionex) { thrownewConcurrentModificationException(); } } publicEremove(intindex) { // 进行index是否越界的判断rangeCheck(index); checkForComodification(); Eresult = parent.remove(parentOffset + index); this.modCount = parent.modCount; this.size--; returnresult; } publicEremove(intindex) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; EoldValue = elementData(index); intnumMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; returnoldValue; }1、先进行下标是否越界的判断,获取 index 处的元素值(这是要删除的值)
2、然后进行元素拷贝,把 index 后面的元素往前拷贝
privatevoidensureCapacityInternal(intminCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } privatevoidensureExplicitCapacity(intminCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } privatevoidgrow(intminCapacity) { // overflow-conscious codeintoldCapacity = elementData.length; // 扩容的代码:这里做了位运算,相当于数组扩容了1.5倍intnewCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 随后进行元素拷贝elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }现在假定场景:arraylist 中已经有 10 个元素类,要放第 11 个元素。
此时进行容量检测,出现问题:空间大小不够。
解决方法:此时进行数组扩容右位移 1(相当于总容量多加 1.5 倍)扩容,老的大小+老大小的一半,进行元素拷贝
publicclassOwnArrayList<E> { privateEdata[]; privateintsize; publicOwnArrayList(intcapacity) { data = (E[]) newObject[capacity]; size = 0; } // 初始化是默认设置大小为20publicOwnArrayList() { this(20); } // 获取数组容量publicintgetCapacity() { returndata.length; } // 获取数组元素个数publicintgetSize() { returnsize; } // 判断数组是否为空publicbooleanisEmpity() { returnsize == 0; } // 获取index索引位置的元素publicEget(intindex) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) thrownewIllegalArgumentException("add failed,the index should >= 0 or <= size"); returndata[index]; } // 修改index索引位置的元素为epublicvoidset(intindex, Ee) { if (index < 0 || index >= size) thrownewIllegalArgumentException("add failed,the index should >= 0 or <= size"); data[index] = e; } // 在数组中间插入一个元素publicvoidadd(intindex, Eelement) { if (size == data.length) { thrownewIllegalArgumentException("AddLast failed,array has already full"); } if (index < 0 || index > size) { thrownewIllegalArgumentException("add failed,the index should >= 0 or <= size"); } for (inti = size - 1; i >= index; i--) { data[i + 1] = data[i]; } data[index] = element; size++; } // 向数组元素末尾添加一个元素publicvoidaddLast(Eelement) { add(size,element); } // 在数组头部插入一个元素publicvoidaddFirst(Eelement) { add(0, element); } // 判断是否含有元素publicbooleancontains(Ee) { for (inti = 0; i < size; i++) if (data[i] == e) returntrue; returnfalse; } // 查找元素e的位置publicintfind(Ee) { for (inti = 0; i < size; i++) { if (data[i] == e) { returni; } } return -1; } // 删除index位置的元素publicEremove(intindex) { if (index < 0 || index > size) { thrownewIllegalArgumentException("index should be 0 to size"); } Eremove_element = data[index]; for (inti = index + 1; i < size; i++) { data[i - 1] = data[i]; } size--; returnremove_element; } // 删除末尾元素// 注意:这是逻辑删除,但是size的大小已经做了相应的减少,所以从实际意义上我们外界并不能访问到末尾元素的值publicEremovelast() { returnremove(size - 1); } // 删除开头元素publicEremoveFirst() { returnremove(0); } // 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小privatevoidresize(intnewCapacity) { newCapacity = getCapacity()*2; E[] newData = (E[]) newObject[newCapacity]; for (inti = 0; i < size; i++) newData[i] = data[i]; data = newData; } }如果有人问你 ArrayList 知多少,我觉得可以从这几个方面出发:
ArrayList 的底层是基于数组进行的,进行随机位置的插入和删除、以及扩容时性能很差,但进行随机的读和取时速度却很快。
接着可以从源码的角度分析 add、remove、set、get、数组扩容拷贝的过程场景。
最后也是特别重要的一点,就是要积极掌握主动性,延伸出 LinkedList 的特点、源码、两者间的对比等。
注:当需要动态数组时我们通常使用 ArrayList 而不是使用类似的 vector,这里有一点说明一下,就是尽管 Vector 的方法都是线程安全的,但其在单线程下需要花费的时间更多,而 ArrayList 尽管不是线程安全的,但其花费的时间很少。
- JDK 集合框架 ArrayList 源码
- 《Core.Java.Volume.I.Fundamentals.11th.Edition》