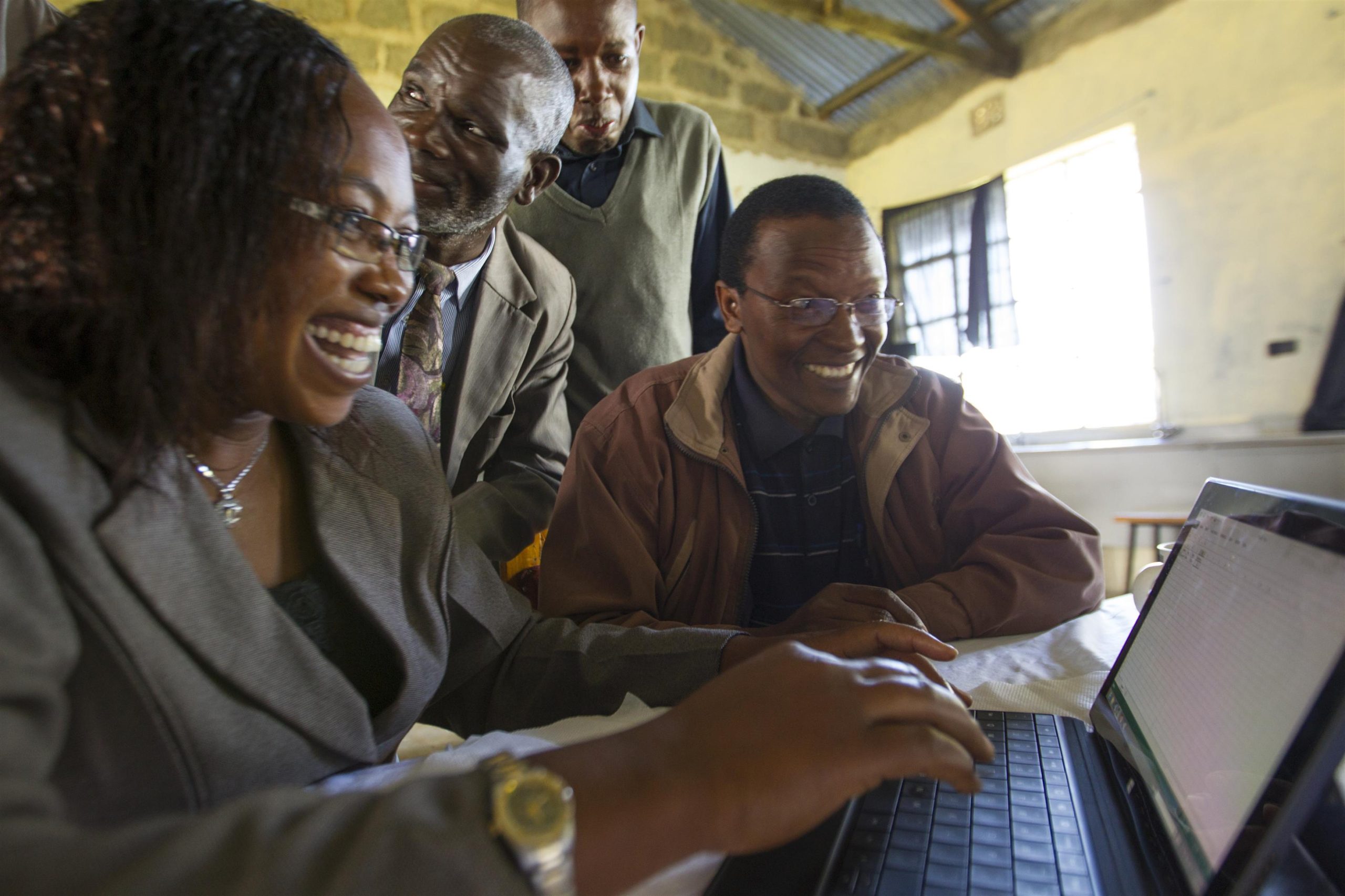
White space networks haven't exactly revolutionized Internet access in the US, but that doesn't mean the technology can't have a major impact in countries that lack consistent access to the Internet. The latest project showing the power of white spaces is unfolding in Kenya, where a solar-powered network is bringing the Internet to people who aren't even connected to an electric grid.
Microsoft deployed the network last month in conjunction with Kenyan government officials. It is serving a health care clinic in Burguret, a primary and secondary school in Male (that's pronounced "mah-lay"), a secondary school in Gakawa, and a library in Laikipia. The network will be expanded to 20 locations in the coming months.
"Down in the valley, nobody has electricity," Paul Garnett, director of technology policy at Microsoft, told Ars. Garnett has been shuttling back and forth between the US and Kenya to get the white spaces network up and running, and he gave me an update on the project in a recent phone interview.
Some of these areas did have mobile Internet access, but "it's so expensive that nobody ever uses it," Garnett said. Electricity isn't completely unavailable, but it is sparse. In one case, a school has electricity going to the principal's office but nowhere else, he said.
That's where solar power comes in. 4.5 kilowatt hours (kWh) of energy per day are derived from 7-square-meter panels.
"During the day the solar panel is providing enough to run the network and provide some charging capability, and then in evenings there is this battery backup that can continue to provide broadband access, plus you have excess capacity for overnight charging," Garnett said. "Think of the school scenario where you've got a computer lab that the kids can use during of the day, and drain down the batteries in the tablets during the day. And then in the evening you have a charging station where all the tablets are plugged in and can recharge overnight."




 Loading comments...
Loading comments... 